Digital signal processing

This dataset contains electrocardiography, electromyography, accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer signals that were measured in different scenarios using wearable equipment on 13 subjects:
- Weight movement in a horizontal position at an angle of approximately 45°.
- Vertical movement of the weights from the table to the floor and back.
- Moving the weights vertically from the table to the head and back.
- Rotational movement of the wrist while holding the weights with the arm extended, see Figure ~\ref{fig2}.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
Image super-resolution (SR) has been an active research problem which has recently received renewed interest due to the introduction of new technologies such as deep learning. However, the lack of suitable criteria to evaluate the SR performance has hindered technology development. In this paper, we fill a gap in the literature by providing the first publicly available database as well as a new image quality assessment (IQA) method specifically designed for assessing the visual quality of super-resolved images (SRIs).
- Categories:
 103 Views
103 ViewsThis dataset contains Wi-Fi sensing data using Channel State Information (CSI) for various sleep disturbance parameters, from respiratory disturbances, to motion-based disturbances from posture shifts, leg restlessness and confusional arousals.The Wi-Fi CSI data was collected using the Wi-Fi module on the ESP32 Microcontroller units using the esp32-csi-tool.The Wi-Fi CSI respiratory disturbance data is accompanied by respiration belt data taken with the Wi-Fi measurements simultaneously using the Neulog NUL-236 respiration belt logger as ground truth.
- Categories:
 829 Views
829 Views
Common Randomness (CR) can be considered as a resource in our future communication systems that will assist in various operations, such as cryptographic encryption in wireless communication, improving identification capacity for identification codes. In wireless communication, CR can be conveniently generated by reading the reciprocal channel properties between two wireless terminals, and by sending pilot signals to each other using the time division duplexing (TDD)-based half-duplexing method. In the channel probing stage, reciprocal channel characteristics are measured.
- Categories:
 147 Views
147 ViewsThe limited availability of Guitar notes datasets hinders the training of any artificial intelligence model in this field. TaptoTab dataset aims to fill this gap by providing a collection of notes recordings. This dataset is collected as part of an honours project at the Faculty of Computer and Information Sciences, Ain Shams University. The dataset is composed of audio data that has been self-collected, focusing on capturing a comprehensive range of guitar notes. The dataset consists of recordings of guitar notes played on each of the six strings, covering up to the 12th fret.
- Categories:
 607 Views
607 Views
This dataset comprises radar-acquired signals from 15 subjects walking on a treadmill, aimed at exploring methodologies for non-contact vital sign detection under conditions of significant body movement. Each subject participated in four experimental sessions, where radar data were collected using two Continuous Wave (CW) radars positioned to capture signals from the front and back of the subject. The data includes both raw and demodulated signals synchronized with ground-truth data obtained from a BioPac system.
- Categories:
 98 Views
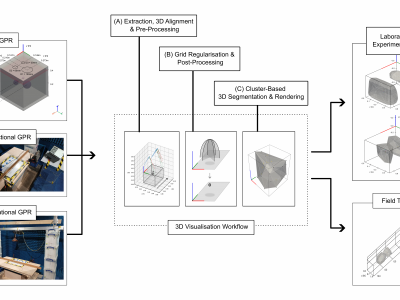
98 ViewsGround Penetrating Radar (GPR) facilitates the detection and localisation of subsurface structural anomalies in critical transport infrastructure (e.g. tunnels), better informing targeted maintenance strategies. However, conventional fixed-directional systems suffer from limited coverage - especially of less-accessible structural aspects (e.g. crowns) - alongside unclear visual output of anomaly spatial profiles, both for physical and simulated datasets.
- Categories:
 496 Views
496 Views
This dataset is utilized for the research of blind identification of CPM signal modulation order. The signal parameters in the dataset range as follows: modulation index from 0.125 to 1, modulation order of 2, 4, 8, pulse types including REC, RC, SRC, TFM, and GMSK, and correlation lengths of 1 to 8. The signals are oversampled by a factor of 10, transmitted through an additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) channel, and the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) ranges from 0 to 30dB.
- Categories:
 70 Views
70 Views
Data set used in an IEEE TIM paper where the objectives of this paper are to test an open-source phase noise analyzer, the direct digital phase noise measurement bench developed by A. Holme (called AH analyzer in this paper), and compare it to a commercial phase noise analyzer, the 53100A.
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views