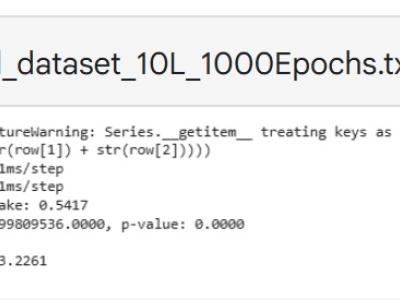
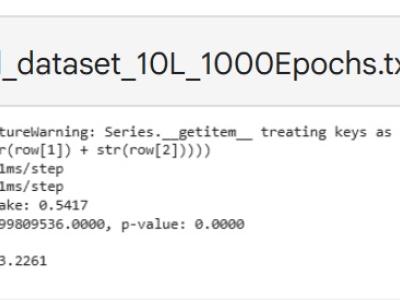
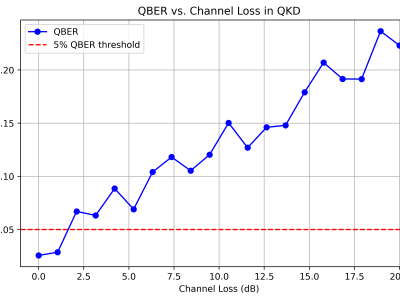
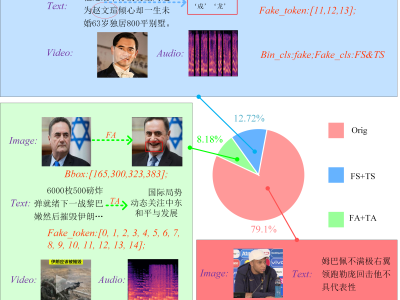
Advanced Metering Infrastructure is prone to cyber threats and Distributed Denial of Service is renowned attack that threatens critical infrastructure. Intrusion detection schemes proposed in earlier works consider the network specific parameters for intrusion detection rather than physical layer parameters. Hence, the proposal considers the physical layer parameters in detecting distributed denial of service attack through abnormal energy consumption pattern of the Data concentrator in the advanced metering infrastructure.
- Categories: