Remote Sensing

The Aerial Image Segmentation Dataset (AISD) is a high-resolution semantic segmentation dataset designed specifically for extracting buildings and roads. The original image is sourced from the online remote sensing images provided by OpenStreetMap and manually annotated. In our experiment, we selected building data from the Potsdam and Tokyo regions. The original image size for Potsdam was 3296 × 3296 pixels, while for Tokyo it was 2500 × 2500 pixels. In this dataset, we cropped the target area image into a 512 × 512 size image.
- Categories:
 5 Views
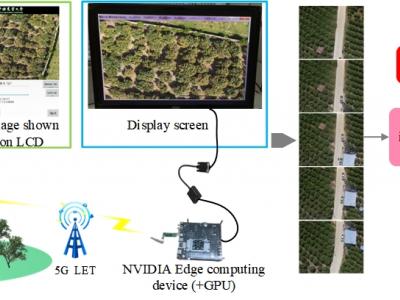
5 ViewsThe system consists of an UAVs remote sensing system and an edge computing system. The core components of the UAVs remote sensing system mainly consist of the imaging system K510 development board and a 5G module. The K510 comes equipped with a camera and an LCD screen. The edge computing system constructed in this paper utilizes the NVIDIA Jetson series development kit, which comes with a GPU module to enhance digital image processing capabilities. The captured raw images are stitched and displayed on the NVIDIA Jetson edge computing platform using our designed improved SFIT algorithm.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 ViewsHigh-quality annotated datasets from diverse scenarios play a crucial role in the development of deep learning algorithms. However, due to the strict access limitations of space-based infrared satellite platforms, space-based infrared small target datasets are scarce. Therefore, we have developed the MIRSat-QL dataset, based on a space-based infrared satellite platform, for space-based dynamic scene infrared target detection. Our data is synthesized from space-based infrared satellite images and ground-based infrared cameras capturing airborne targets. The specifics are as follows。
- Categories:
 118 Views
118 ViewsHigh-quality annotated datasets from diverse scenarios play a crucial role in the development of deep learning algorithms. However, due to the strict access limitations of space-based infrared satellite platforms, space-based infrared small target datasets are scarce. Therefore, we have developed the MIRSat-QL dataset, based on a space-based infrared satellite platform, for space-based dynamic scene infrared target detection. Our data is synthesized from space-based infrared satellite images and ground-based infrared cameras capturing airborne targets. The specifics are as follows。
- Categories:
 58 Views
58 ViewsObject detection is an important and challenging problem in computer vision. Although the past decade has witnessed major advances in object detection in natural scenes, such successes have been slow to aerial imagery, not only because of the huge variation in the scale, orientation and shape of the object instances on the earths surface, but also due to the scarcity of wellannotated datasets of objects in aerial scenes.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 ViewsExtracting ships from complex backgrounds is the bottleneck of ship detection in high-resolution optical satellite images. In this letter, we propose a nearly closed-form ship rotated bounding box space used for ship detection and design a method to generate a small number of highly potential candidates based on this space. We first analyze the possibility of accurately covering all ships by labeling rotated bounding boxes. Moreover, to reduce search space, we construct a nearly closed-form ship rotated bounding box space.
- Categories:
 110 Views
110 ViewsExtracting ships from complex backgrounds is the bottleneck of ship detection in high-resolution optical satellite images. In this letter, we propose a nearly closed-form ship rotated bounding box space used for ship detection and design a method to generate a small number of highly potential candidates based on this space. We first analyze the possibility of accurately covering all ships by labeling rotated bounding boxes. Moreover, to reduce search space, we construct a nearly closed-form ship rotated bounding box space.
- Categories:
 76 Views
76 ViewsSubstantial efforts have been devoted more recently to presenting various methods for object detection in optical remote sensing images. However, the current survey of datasets and deep learning based methods for object detection in optical remote sensing images is not adequate. Moreover, most of the existing datasets have some shortcomings, for example, the numbers of images and object categories are small scale, and the image diversity and variations are insufficient. These limitations greatly affect the development of deep learning based object detection methods.
- Categories:
 85 Views
85 Views
This study utilizes the open-source datasets FAIR1M and HRSC2016 as foundational resources to construct an optical remote sensing image dataset for rotated ship target detection. The dataset encompasses nine ship categories: Dry-Cargo-Ship, Engineering-Ship, Fishing-Boat, Motorboat, Tugboat, Passenger-Ship, Warship, Liquid-Cargo-Ship, and Other-Ship.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views