Machine Learning

The DroneDetect dataset consists of 7 different models of popular Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) including the new DJI Mavic 2 Air S, DJI Mavic Pro, DJI Mavic Pro 2, DJI Inspire 2, DJI Mavic Mini, DJI Phantom 4 and the Parrot Disco. Recordings were collected using a Nuand BladeRF SDR and using open source software GNURadio. There are 4 subsets of data included in this dataset, the UAS signals in the presence of Bluetooth interference, in the presence of Wi-Fi signals, in the presence of both and with no interference.
- Categories:
 12758 Views
12758 ViewsThe objective of this dataset is the fault diagnosis in diesel engines to assist the predictive maintenance, through the analysis of the variation of the pressure curves inside the cylinders and the torsional vibration response of the crankshaft. Hence a fault simulation model based on a zero-dimensional thermodynamic model was developed. The adopted feature vectors were chosen from the thermodynamic model and obtained from processing signals as pressure and temperature inside the cylinder, as well as, torsional vibration of the engine’s flywheel.
- Categories:
 4940 Views
4940 Views
Cyber-physical systems (CPS) have been increasingly attacked by hackers. Recent studies have shown that CPS are especially vulnerable to insider attacks, in which case the attacker has full knowledge of the systems configuration. To better prevent such types of attacks, we need to understand how insider attacks are generated. Typically, there are three critical aspects for a successful insider attack: (i) Maximize damage, (ii) Avoid detection and (iii) Minimize the attack cost.
- Categories:
 307 Views
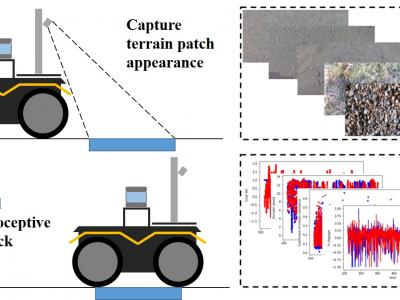
307 ViewsThe Jackal UGV, from Clearpath Robotics, was used as the data collecting platform. This skid-steer four-wheel-drive vehicle comes with an onboard IMU, two DC motors with encoders that measure wheel angular speeds, and current sensors that measure motor current outputs. On each side of the robot, the front wheel and back wheel are jointed with a gearbox and so spin together at the same rate and direction. The IMU provided vehicle attitude measurements in terms of Euler angles, as well as linear acceleration and angular rate of the vehicle body in three Euclidean axes.
- Categories:
 1207 Views
1207 ViewsThe data set contains 152 measurements of room impulse responses for direction of arrival estimation, using a compact three-channel microphone array. Sources are placed at 10-degree intervals from -90 to 90 degrees in the azimuth plane at range 150 cm. There are also 5 off-grid measurement positions and 6 off-range positions - at ranges 1 m, 2 m, 2.5 m and 3 m. The measurements are performed in a furnished classroom, which is approximately rectangular and of dimensions 9 x 6 x 3 m. The reverberation time is 0.4 s.
- Categories:
 861 Views
861 Views
The dermoscopic images considered in the paper "Dermoscopic Image Classification with Neural Style Transfer" are available for public download through the ISIC database (https://www.isic-archive.com/#!/topWithHeader/wideContentTop/main). These are 24-bit JPEG images with a typical resolution of 768 × 512 pixels. However, not all the images in the database are in satisfactory condition.
- Categories:
 1608 Views
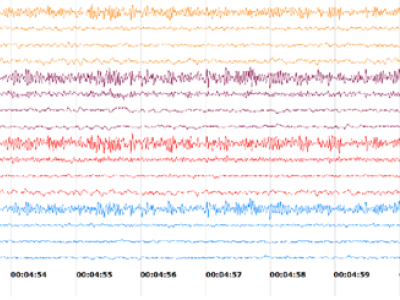
1608 ViewsThis dataset consists of EEG data of 40 epileptic seizure patients (both male and female) of age from 4 to 80 years. The raw data was collected from Allengers VIRGO EEG machine at Medisys Hospitals, Hyderabad, India. The EEG electrodes were placed according to 10 – 20 International standard. The EEG data was recorded from 16 channels (FP2-F4, F4-C4, C4-P4, P4-O2, FP1-F3, F3-C3, C3-P3, P3-O1, FP2-F8, F8-T4, T4-T6, T6-O2, FP1-F7, F7-T3, T3-T5, and T5-O1) at 256 samples per second.
- Categories:
 11105 Views
11105 ViewsReverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is currently the gold standard in COVID-19 diagnosis. It can, however, take days to provide the diagnosis, and false negative rate is relatively high. Imaging, in particular chest computed tomography (CT), can assist with diagnosis and assessment of this disease. Nevertheless, it is shown that standard dose CT scan gives significant radiation burden to patients, especially those in need of multiple scans.
- Categories:
 2968 Views
2968 Views