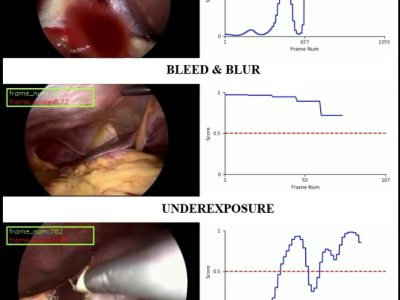
In today’s digital ecosystem, verifying the authenticity of identity documents is essential for secure access control and digital trust. Sectors such as finance, education, government, and employment frequently rely on scanned or digital versions of documents like Aadhaar cards, PAN cards, Voter IDs, Driving Licenses, and Passports. However, this convenience introduces risks related to document forgery and fraudulent activity.
- Categories: