
The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) Reanalysis v.5 (ERA5)-Land and Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) land surface temperature.
- Categories:

The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) Reanalysis v.5 (ERA5)-Land and Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) land surface temperature.

The multi-modal MR、CT、PET、SPECT image

<p>ImageNet is a large-scale visual database widely used in the field of computer vision, especially for object recognition tasks. It contains millions of labeled images, organized into multiple categories, and is used for training and evaluating image classification models. ImageNet datasets are widely used for training deep learning models, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). ILSVRC2012 (ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge 2012) is a part of ImageNet and is a competition for image classification and object detection.

The IARPA Space-Based Machine Automated Recognition Technique (SMART) program was one of the first large-scale research program to advance the state of the art for automatically detecting, characterizing, and monitoring large-scale anthropogenic activity in global scale, multi-source, heterogeneous satellite imagery. The program leveraged and advanced the latest techniques in artificial intelligence (AI), computer vision (CV), and machine learning (ML) applied to geospatial applications.

This dataset is a large-scale video benchmark constructed for RGB-Thermal (RGB-T) object tracking tasks, featuring the following key characteristics:
1. **Scale & Diversity**
- Contains 234,000 total frames, with sequences up to 8,000 frames
- Covers diverse scenarios and complex environmental conditions
- Currently the largest publicly available RGB-T dataset in the field
2. **Precise Multimodal Alignment**
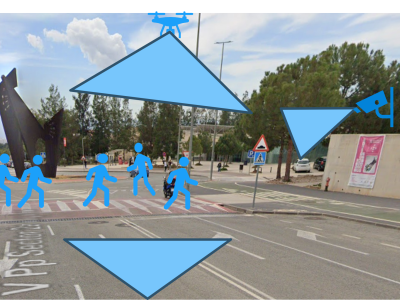
This dataset was produced as part of the NANCY project (https://nancy-project.eu/), with the aim of using it in the fields of communication and computer vision. Within the dataset are contained three different scenarios, each of which has three videos. All three videos were captured by different devices; a vehicle-mounted unit, a roadside unit (RSU), and a drone.

FLAME2-DT (Forest Fire Detection Dataset with Dual-modality Labels) is a comprehensive multi-modal dataset specifically designed for UAV-based forest fire detection research. The dataset consists of 1,280 paired RGB-thermal infrared images captured by a Mavic 2 Enterprise Advanced UAV system, with high-resolution (640×512) and precise pixel-level annotations for both fire and smoke regions. This dataset addresses critical challenges in forest fire detection by providing paired multi-modal data that captures the complementary characteristics of visible light and thermal imaging.
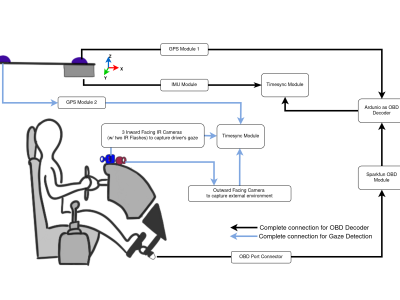
Repeated Route Naturalistic Driving Dataset (R2ND2) is a dual-perspective dataset for driver behavior analysis constituent of vehicular data collected using task-specific CAN decoding sensors using OBD port and external sensors, and (b) gaze-measurements collected using industry-standard multi-camera gaze calibration and collection system. Our experiment is designed to consider the variability associated with driving experience that depends on the time of day and provides valuable insights into the correlation of these additional metrics on driver behavior.

Hyperspectral imaging (HSI) has become a pivotal tool for environmental monitoring, particularly in identifying and analyzing hydrocarbon spills. This study presents an Internet of Things (IoT)-based framework for the collection, management, and analysis of hyperspectral data, employing a controlled experimental setup to simulate hydrocarbon contamination. Using a state-of-the-art hyperspectral camera, a dataset of 116 images was generated, encompassing temporal and spectral variations of gasoline, thinner, and motor oil spills.