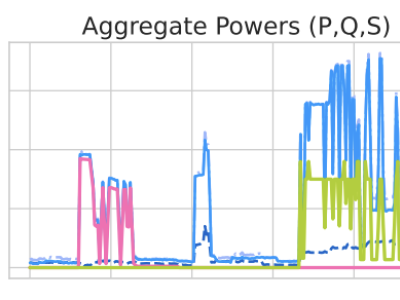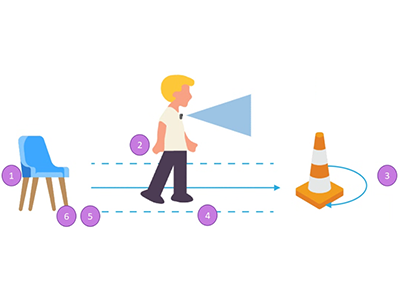
This dataset aims to support research on temporal segmentation of the Timed Up and Go (TUG) test using a first-person wearable camera. The data collection includes a training set of 8 participants and a test set of 60 participants. Among the 8 participants, the test was completed at both a normal walking pace and a simulated slower walking pace to mimic elderly movement patterns. The 60 participants were randomly divided into two groups: one group completed the test at a normal walking pace, and the other group simulated slower walking speed to mimic elderly movement patterns.
- Categories: