Machine Learning

This MATLAB script implements a reinforcement learning (RL) approach to optimize IRS phase configurations in a MIMO wireless system. The implementation features a basic MIMO setup with a 16-element IRS operating at 12 GHz (mid-band frequency). Using the policy gradient method with a two-layer neural network, it learns optimal phase shifts while considering user mobility and Rician fading channels. The system models both direct and IRS-reflected paths, incorporating realistic path loss and channel conditions.
- Categories:
 165 Views
165 ViewsIn this dataset, a human detecting model using with UWB radar technology is presented. Two distinct datasets were created using the UWB radar device, leveraging its dual features. Data collection involved two main scenarios, each containing multiple sub-scenarios. These sub-scenarios varied parameters like the position, distance, angle, and orientation of the human subject relative to the radar. Unlike conventional approaches that rely on signal processing or noise/background removal, this study uniquely emphasizes analyzing raw UWB radar data directly.
- Categories:
 644 Views
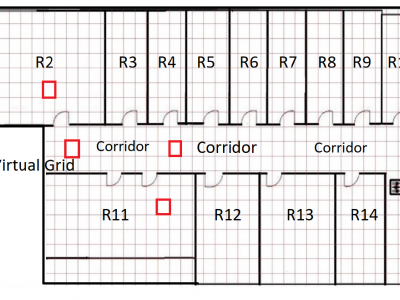
644 ViewsThe JU-Impact Radiomap Dataset is a comprehensive dataset designed for research and development in indoor positioning systems. It comprises 5431 instances characterized by readings from 105 static Wi-Fi Access Points (APs) and spans 152 distinct virtual grids. Each virtual grid represents a 1x1 square meter area, derived by dividing a physical floor of a university building into reference coordinate points (x, y). The dataset was collected over a period of 21 days using four mobile devices: Samsung Galaxy Tab, Moto G, Redmi Note 4, and Google Pixel.
- Categories:
 164 Views
164 Views
CodePromptEval is a dataset of 7072 prompts designed to evaluate five prompt techniques (few-shot, persona, chain-of-thought, function signature, list of packages) and their effect on the correctness, similarity, and quality of complete functions generated. Each data point in the dataset includes a function generation task, a combination of prompt techniques to be applied, the prompt in natural language that applied the prompt techniques, the ground truth of the functions (human-written functions based on CoderEval dataset by Yu et al.), the tests to evaluate the correctness of the generate
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
Annotated 1,000 misalignment from the SDGSAT-1 glimmer imagery, divided into train, valid, and test sets with a ratio of 7:2:1 for the object detection task.
- Categories:
 45 Views
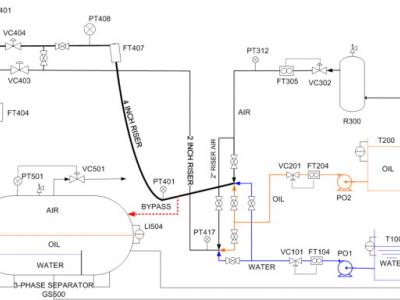
45 ViewsDateset of the Three-Phase Flow Facility. The Three-phase Flow Facility at Cranfield University is designed to provide a controlled and measured flow rate of water, oil and air to a pressurized system. Fig. 1 shows a simplified sketch of the facility. The test area consists of pipelines with different bore sizes and geometries, and a gas and liquid two-phase separator (0.5 m diameter and 1.2 m high) at the top of a 10.5 m high platform. It can be supplied with single phase of air, water and oil, or a mixture of those fluids, at required rates.
- Categories:
 264 Views
264 ViewsThe analysis suggests various innovative ideas to improve English instruction, with an emphasis on current technologies and an inclusive approach. These include using AI as a peer tutor, exploring virtual reality to create immersive learning environments, analyzing data to create customized learning materials, integrating local cultural values into instructional materials, implementing a technology-based inclusive learning model, implementing a policy for digital advancement in education, and making the most of contemporary learning resources.
- Categories:
 129 Views
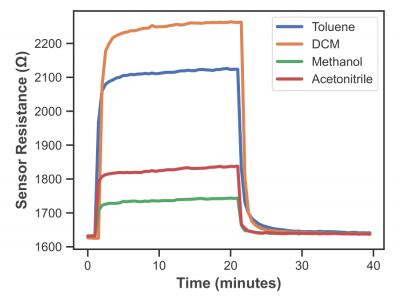
129 ViewsThis dataset contains 2,016 sensor responses collected from an array of conductive carbon-black polymer composite sensors, exposed to four target analytes—acetonitrile, dichloromethane (DCM), methanol, and toluene—at nine distinct concentration levels ranging from 0.5% to 20% P/P₀. Each sensor was exposed to the analytes for 20 minutes, followed by 20 minutes of nitrogen flushing to restore the baseline. The data consists of 80 time points (one every 30 seconds) per response, with each time point representing the sensor's resistance to a specific analyte concentration.
- Categories:
 110 Views
110 Views
All the healthcare facilites in this dataset were collected from the MOH 2018 list of Uganda healthcare facilites (https://library.health.go.ug/sites/default/files/resources/National%20Health%20Facility%20MasterLlist%202017.pdf) Additional features were scraped using the Google Maps API and additionally from some of the websites of the healthcare facilities themselves.
- Categories:
 70 Views
70 Views