Sensors

A multimodal dataset is presented for the cognitive fatigue assessment of physiological minimally invasive sensory data of Electrocardiography (ECG) and Electrodermal Activity (EDA) and self-reporting scores of cognitive fatigue during HRI. Data were collected from 16 non-STEM participants, up to three visits each, during which the subjects interacted with a robot to prepare a meal and get ready for work. For some of the visits, a well-established cognitive test was used to induce cognitive fatigue.
- Categories:
 143 Views
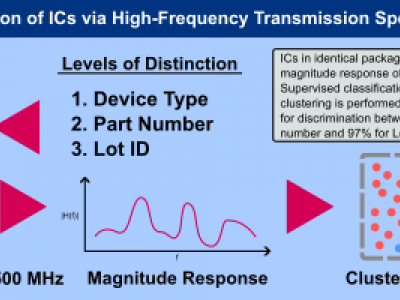
143 ViewsHigh-frequency transmission spectroscopy (HFTS) is a novel technique for the classification of a wide range of materials in biomedical, environmental, security, and manufacturing domains. HFTS is based on the fusion of scattering parameter measurements and machine learning classification techniques to identify materials of interest in novel environments. This work seeks to demonstrate the efficacy of HFTS in the domain of integrated circuit classification.
- Categories:
 97 Views
97 Views
ZJT datasets: It was collected from the production line of China Tobacco Zhejiang Industrial Company. The data was sampled every two seconds for a week from 162 sensors deployed on a variety of production devices (e.g., paper cut-ting wheel, power supply, etc.). Since ZJT is a dataset from real-world production line, it does not contain serious anoma-lies from accidents or attacks. Thus, we treat the states of transforming between different producing modes as anoma-lies. The ratio of normal states to abnormal states is 4:1.
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views
This study introduces a novel soil texture dataset designed to overcome geographic constraints and improve the generalization of classification models. Using the USDA soil classification triangle as a framework, the dataset is systematically generated by combining pure sand, silt, and clay in varying proportions to create diverse soil texture classes. The soil mixtures are captured using a multispectral sensor with seven bands, ensuring a rich representation of spectral information.
- Categories:
 142 Views
142 Views
This study identifies representative sensors for monitoring fan performance by analyzing vibration data collected from piezoelectric sensors during various operational modes. The dataset, which includes measurements at a rate of 300 samples/sec from 10 sensors, covers six modes of operation: Maximum Speed, Maximum Speed with Oscillation, Minimum Speed, Minimum Speed with Oscillation, Minimum to Maximum Speed, and a comprehensive dataset combining all modes.
- Categories:
 96 Views
96 Views
A method of broadening frequency bandwidth and improving sensitivity of a Fabry-Pérot (F-P) geophone is proposed, and the corresponding high-performance device is designed and demonstrated experimentally.
- Categories:
 10 Views
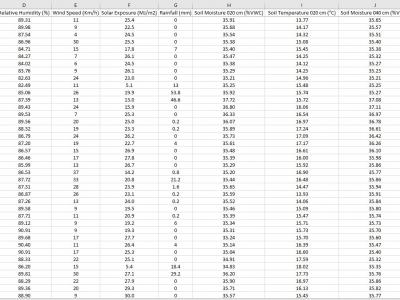
10 ViewsThe data is collected from the deployed IoT sensor node at a pilot farm in Narrabri, Australia. The dataset includes information about soil characteristics such as soil moisture and soil temperature at 20-40-60 cm depth. The sensor node also provides information about environmental influencers, which are critical in constructing machine learning models to predict Evapotranspiration in diverse soil and environmental conditions.
- Categories:
 777 Views
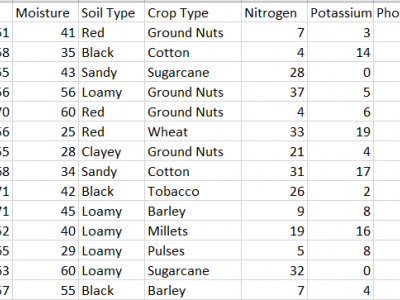
777 ViewsThis dataset provides comprehensive data for predicting the most suitable fertilizer for various crops based on environmental and soil conditions. It includes environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and moisture, along with soil and crop types, and nutrient composition (Nitrogen, Potassium, and Phosphorous). The target variable is the recommended fertilizer name.
The data is already pre-processed without anu Null values.
- Categories:
 1651 Views
1651 Views
The necessity for strong security measures to fend off cyberattacks has increased due to the growing use of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technologies. This research introduces IoTForge Pro, a comprehensive security testbed designed to generate a diverse and extensive intrusion dataset for IIoT environments. The testbed simulates various IIoT scenarios, incorporating network topologies and communication protocols to create realistic attack vectors and normal traffic patterns.
- Categories:
 315 Views
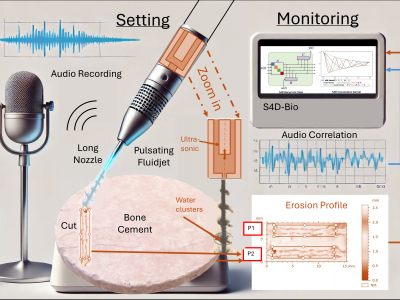
315 ViewsThis dataset comprises extensive multi-modal data related to the experimental study of ultrasonically excited pulsating fluid jets used for bone cement removal. Conducted at the Institute of Geonics, Ostrava, Czech Republic, the study explores the effect of varying standoff distances on erosion profiles, under controlled parameters including a fixed nozzle diameter, sonotrode frequency, supply pressure, and robot arm velocity. The dataset includes numerical data representing ablation profiles, captured as a large CSV file, and audio recordings captured using a high-resolution microphone.
- Categories:
 200 Views
200 Views