Medical Imaging
The Numerical Latin Letters (DNLL) dataset consists of Latin numeric letters organized into 26 distinct letter classes, corresponding to the Latin alphabet. Each class within this dataset encompasses multiple letter forms, resulting in a diverse and extensive collection. These letters vary in color, size, writing style, thickness, background, orientation, luminosity, and other attributes, making the dataset highly comprehensive and rich.
- Categories:
 517 Views
517 Views
- Categories:
 348 Views
348 ViewsAutism spectrum disorder (ASD) is characterized by qualitative impairment in social reciprocity, and by repetitive, restricted, and stereotyped behaviors/interests. Previously considered rare, ASD is now recognized to occur in more than 1% of children. Despite continuing research advances, their pace and clinical impact have not kept up with the urgency to identify ways of determining the diagnosis at earlier ages, selecting optimal treatments, and predicting outcomes. For the most part this is due to the complexity and heterogeneity of ASD.
- Categories:
 1880 Views
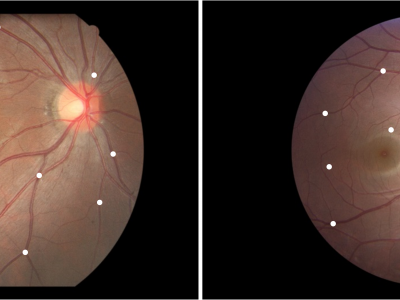
1880 ViewsFundus Image Myopia Development (FIMD) dataset contains 70 retinal image pairs, in which, there is obvious myopia development between each pair of images. In addition, each pair of retinal images has a large overlap area, and there is no other retinopathy. In order to perform a reliable quantitative evaluation of registration results, we follow the annotation method of Fundus Image Registration (FIRE) dataset [1] to label control points between the pair of retinal images with the help of experienced ophthalmologists. Each image pair is labeled with
- Categories:
 498 Views
498 ViewsThis dataset contains MRI data acquired approximately 20 minutes before ("Pre-ablation") and 20-40 minutes after ("Post-ablation") MR-guided focused ultrasound thermal ablations in the muscle tissue (quadriceps) in four (n=4) New Zealand white rabbits. MR images include MR thermometry acquired with the proton resonance frenquency method, ADC maps (b=0,400), T2-weighted, and pre- and post-contrast enhanced T1-weighted images. All MRI acquisitions were 3D except for the ADC acquisition, which was 2D multi-slice.
- Categories:
 156 Views
156 Views
This dataset is collected from Kaggle ( https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/masoudnickparvar/brain-tumor-mri-dataset ). This dataset is a combination of the following three datasets :
- Categories:
 12323 Views
12323 ViewsThe demand for artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare is rapidly increasing. However, significant challenges arise from data scarcity and privacy concerns, particularly in medical imaging. While existing generative models have achieved success in image synthesis and image-to-image translation tasks, there remains a gap in the generation of 3D semantic medical images. To address this gap, we introduce Med-DDPM, a diffusion model specifically designed for semantic 3D medical image synthesis, effectively tackling data scarcity and privacy issues.
- Categories:
 2866 Views
2866 Views
The morphological characteristics of skeletal muscles, such as fascicle orientation, fascicle length, and muscle thickness, contain valuable mechanical information that aids in understanding muscle contractility and excitation due to commands from the central nervous system. Ultrasound (US) imaging, a non-invasive measurement technique, has been employed in clinical research to provide visualized images that capture morphological characteristics. However, accurately and efficiently detecting the fascicle in US images is challenging.
- Categories:
 214 Views
214 Views
Elastography is a non-invasive technique to detect tissue anomalies via the local elastic modulus using shear waves. Commonly shear waves are produced via acoustic focusing or the use of mechanical external sources, shear waves may result also naturally from cavitation bubbles during medical intervention, for example from thermal ablation. Here, we measure the shear wave emitted from a well-controlled single laser-induced cavitation bubble oscillating near a rigid boundary. The bubbles are generated in a transparent tissue-mimicking hydrogel embedded with tracer particles.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views