Medical Imaging
The ultrasound video data were collected from two sets of neck ultrasound videos of ten healthy subjects at the Ultrasound Department of Longhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Each subject included video files of two groups of LSCM, LSSCap, RSCM, and RSSCap. The video format is avi.
The MRI training data were sourced from three hospitals: Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Huadong Hospital, Fudan University; and Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital.
- Categories:
 575 Views
575 Views
This collection of medical image datasets is a valuable resource for anyone involved in medical imaging and disease research. It includes a variety of images from different medical fields, all designed to support research in diagnosis and treatment. The datasets cover chest CT-scans, lung radiography, brain MRI, retinal imaging, and gastrointestinal tract imaging. The chest CT-scan dataset includes 867 images of normal lungs and three types of lung cancer—adenocarcinoma, large cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma—providing essential data for understanding lung cancer.
- Categories:
 2546 Views
2546 Views
This data abstract pertains to an ultrasound imaging dataset that includes imaging data from both CIRS phantoms and human carotid artery cross-sections. The dataset encompasses:
- Categories:
 102 Views
102 ViewsWe introduce two novel datasets for cell motility and wound healing research: the Wound Healing Assay Dataset (WHAD) and the Cell Adhesion and Motility Assay Dataset (CAMAD). WHAD comprises time-lapse phase-contrast images of wound healing assays using genetically modified MCF10A and MCF7 cells, while CAMAD includes MDA-MB-231 and RAW264.7 cells cultured on various substrates. These datasets offer diverse experimental conditions, comprehensive annotations, and high-quality imaging data, addressing gaps in existing resources.
- Categories:
 964 Views
964 Views
Ultrasound (US) provides non-invasive visualization of tissue morphology for musculoskeletal disorders. Spatial Frequency Analysis (SFA) of US images quantitatively characterizes tissue morphology, and has shown the ability to distinguish healthy from pathological tendons. However, the impact of US machine settings on SFA for tendon pathology remains underexplored. Methods: Five participants with unilateral supraspinatus tendon partial tears were imaged bilaterally to examine how variations in US settings (frequency, dynamic range, gain) influence SFA parameters.
- Categories:
 184 Views
184 Views
Machine learning (ML) in the medical domain faces challenges due to limited high-quality data. This study addresses the scarcity of echocardiography images (echoCG) by generating synthetic data using state-of-the-art generative models. We evaluated a cycle-consistent generative adversarial network (CycleGAN), contrastive unpaired translation (CUT) method, and latent diffusion model (Stable Diffusion 1.5).
- Categories:
 180 Views
180 Views<p class="MsoNormal"><span lang="EN-US">This is a dataset about Helicobacter pylori (H.pylori). The dataset consists of 994 pathology images of H. pylori stained using immunohistochemistry. Each image is of size 1916x1010 pixels and is accompanied by an annotation file. The annotations are done using point annotations, where the annotation file records the coordinates of H. pylori in each image.</span><span><span lang="EN-US">The dataset provides a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners working in the field of H.
- Categories:
 384 Views
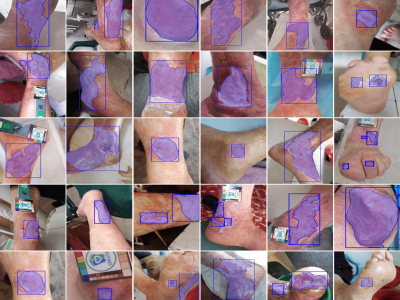
384 ViewsChronic wounds pose an ongoing health concern globally, largely due to the prevalence of conditions such as diabetes and leprosy's disease. The standard method of monitoring these wounds involves visual inspection by healthcare professionals, a practice that could present challenges for patients in remote areas with inadequate transportation and healthcare infrastructure. This has led to the development of algorithms designed for the analysis and follow-up of wound images, which perform image-processing tasks such as classification, detection, and segmentation.
- Categories:
 1266 Views
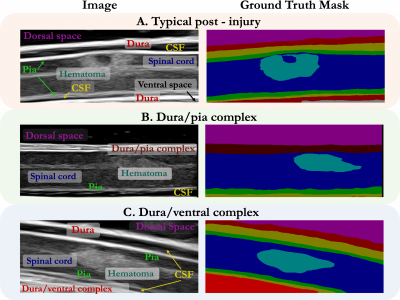
1266 ViewsWhile deep learning has catalyzed breakthroughs across numerous domains, its broader adoption in clinical settings is inhibited by the costly and time-intensive nature of data acquisition and annotation. To further facilitate medical machine learning, we present an ultrasound dataset of 10,223 Brightness-mode (B-mode) images consisting of sagittal slices of porcine spinal cords (N=25) before and after a contusion injury.
- Categories:
 145 Views
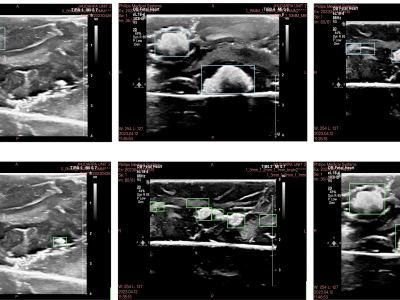
145 ViewsThe removal of surgical tools from the brain is a critical aspect of post-operative care. Surgical sponges such as cotton balls are one of the most commonly retained tools, as they become visually indistinguishable from the surrounding brain tissue when soaked with blood and can fragment into smaller pieces. This can lead to life-threatening immunological responses and invasive reoperation, demonstrating the need for new foreign body object detection methods.
- Categories:
 132 Views
132 Views