Sensors
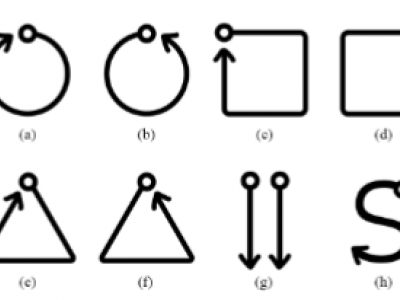
This dataset comprises high-resolution 3-axis accelerometer recordings collected from human participants performing distinct hand gestures, intended for training gesture-based assistive interfaces. Each participant’s raw motion signals are individually organized, enabling both user-specific and generalizable model development. The dataset includes time-series accelerometer data, along with a feature-augmented version containing extracted statistical and temporal descriptors such as RMS, Jerk, Entropy, and SMA.
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 ViewsThis dataset contains 60,000 annotated records modeling UAV-based and IoT sensor-driven agriculture environments. Each record includes UAV imaging data (NDVI, NDRE, RGB damage score), IoT sensor values (NPK, pH, moisture, temperature, humidity), semantic labels (NDI, PDI), and metadata for energy consumption, latency, and service migration. It is designed for validating Digital Twin frameworks, semantic communication models, and Federated Deep Reinforcement Learning (FDRL) in precision farming.
- Categories:
 90 Views
90 Views
Real-time tracking of electricians in distribution rooms is essential for ensuring operational safety. Traditional GPS-based methods, however, are ineffective in such environments due to complex non-line-of-sight (NLOS) conditions caused by dense cabinets and thick walls that obstruct satellite signals. Existing solutions, such as video-based systems, are prone to inaccuracies due to NLOS effects, while wearable devices often prove inconvenient for workers.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 ViewsThis dataset comprises volatile organic compound (VOC) profiles collected from blood culture broth samples using an electronic nose (E-nose) system. The samples include cultures positive for Candida spp., including C. albicans, C. glabrata, C. tropicalis, among others, as well as negative control samples.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
This dataset provides 6D magnetic localization data for surgical instrument tracking, focusing on position and orientation estimation in minimally invasive procedures. It includes various trajectory experiments such as square, circular, saddle-shaped, and helical paths, along with simulated minimally invasive knee surgery and needle sampling experiments. Additionally, it contains dynamic error correction verification data. Data is collected using 16 LIS3MDL magnetometers at 300 Hz, offering both raw and filtered data for algorithm validation.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 ViewsA pothole dataset collected by iPhone 14 pro. Due to the lack of publicly available small-scale pothole point cloud datasets, a custom dataset was created for model performance evaluation. The data collection area is located within the Yujiaotou campus of Wuhan University of Technology and the surrounding road network in Wuhan, China. For data acquisition, an iPhone 14 Pro equipped with a LiDAR scanner was used.
- Categories:
 91 Views
91 Views
This dataset comprises a collection of CSV files containing paired time-series measurements essential for nonlinear compensation research in electrochemical seismometers (MET). Each CSV file, named according to specific magnitude-frequency combinations (magX_freqY.csv), contains two columns: 'origin' representing the original system response and 'target' representing the desired compensated output.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
This study presents a deep learning-based framework for detecting vehicle deceleration patterns using Ultra-Wideband (UWB) Channel Impulse Response (CIR) analysis. Unlike traditional GPS or IMU-based systems, which struggle in GPS-denied environments such as tunnels, the proposed method leverages UWB CIR signal variations to classify two key driving behaviors: rapid deceleration and gradual deceleration. All data were collected from real-world experiments using UWB devices installed on actual vehicles at a professional highway testing site.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
Ultra Wideband (UWB) signals offer high spatio-temporal resolution, penetrability, and low cost, which facilitates accurate characterization of limb features through micro-Doppler (mD) analysis, even with micro random body movements, during the wireless contactless sensing. Due to challenges introduced by arm motions, which may be perpendicular to the radar, we introduce a dual radar arm motion recognition system with light-weighted feature extraction and appropriate data fusion.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views