Biomedical and Health Sciences
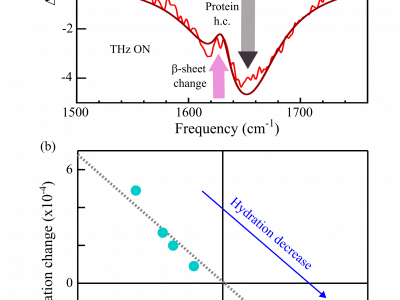
We investigated the effect of CW radiation at 0.6 THz on pathological protein aggregates in the form of amyloid fibrils, i.e. ordered protein complexes linked to neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and Frontotemporal Dementia. To monitor the effect of THz irradiation we exploited mid-infrared (mid-IR) vibrational spectroscopy in the amide-I band range, whose lineshape is known to depend on the protein conformation and on how proteins arrange into ordered supramolecular complexes such as fibrils.
- Categories:
 212 Views
212 Views
The rapid development of highly multiplexed microscopy systems has enabled the study of cells embedded within their native tissue. The rich spatial data provided by these techniques have yielded exciting insights into the spatial features of human disease. However, computational methods for analyzing these high-content images are still emerging, and there is a need for more robust and generalizable tools for evaluating the cellular constituents and underlying stroma captured by high-plex imaging.
- Categories:
 102 Views
102 ViewsA dataset comprising a total of 21 individuals has been meticulously compiled, with 9 individuals identified as exhibiting Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) based on the outcomes derived from the PHQ-9 Questionnaire. The remaining 12 individuals in the dataset are classified as non-MDD.
The dataset encompasses diverse sensor data, including temperature measurements, SpO2 readings, pulse rates, and accelerometer data. It is important to note that all data points were collected within a controlled environment, ensuring reliability and consistency throughout the dataset.
- Categories:
 2431 Views
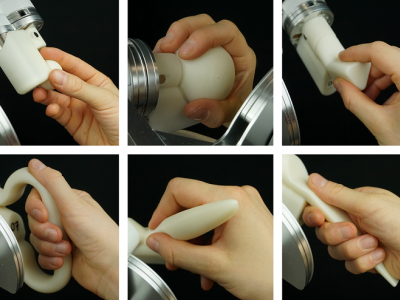
2431 ViewsThis dataset contains the 3D data of nine different grasp type handles that were developed specifically to investigate the influence of the telemanipulator handle on surgical teleoperation tasks with a customized, six degrees of freedom, handleless lambda.6 haptic device (Force Dimension, Nyon, Switzerland). Each of these handles is designed to be grasped with a different grasp type: power disk, quadpod, power sphere, tripod, precision disk, parallel extension, fixed hook, writing tripod, and adducted thumb.
- Categories:
 108 Views
108 ViewsThis is the raw data for the article "Algorithm for Gait Parameters Estimation Based on Heel-Mounted Inertial Sensors", which includes walking data recorded by IMUs and data recorded by an optical motion capture (OMC) system, where the experimental data consisted of three parts:
Validity Experiment Data includes gait data (both IMU and OMC) of 30 participants who were instructed to walk in a straight line within the motion capture area and return upon reaching the end to ensure a sufficient step count.
- Categories:
 443 Views
443 Views<p><span style="color: #3c4043; font-family: Inter, sans-serif; font-size: 14px;">The dataset is collected from 3 MPU9250 sensors connected simultaneously on different positions of the hand. One sensor was placed on the wrist, another between wrist and elbow and another between elbow and shoulder. The dataset contains a 3-axis accelerometer, 3-axis gyroscope and 3-axis magnetometer readings along with a result column in which '1' denoted shaking hand and '0' denoted stable hand.
- Categories:
 832 Views
832 Views
Seventeen male participants (age: 22.8 ± 3.0 years old, height: 1.76 ± 6.2 m, weight: 67.7 ± 5.9 kg, resting heart rate: 66.5 ± 7.0 bpm) without cardiovascular and chronic respiratory problems were recruited. None of the gathered participants had a history of neuromuscular disorders within the past six months. Each participant performed three 30-minute treadmill or terrain running experiences every week in order to maintain his aerobic capability. Participants provided their informed consent after receiving an overview of procedures and potential risks.
- Categories:
 69 Views
69 ViewsManual palpation of organs played a vital role in detecting abnormalities in open surgeries. However, surgeons
have lost this ability with the development of minimally invasive surgeries. This challenge led to the development of artificial sensors for palpating the patient's organs and tissue. The majority of research done is related to improving the measurement of tissue compliance by the development of versatile force sensors for surgical
- Categories:
 847 Views
847 ViewsOCD description. Cell lines A172 and U251: human glioblastoma; MCF7: human breast cancer; MRC5: human lung fibroblast; SCC25: human squamous cell carcinoma. Cultivation condition CTR: cells belonging to the control group - without the addition of chemotherapy; TMZ: cells treated with 50 μM temozolomide in some cultivation step.
Split
- Categories:
 520 Views
520 ViewsTowards an accessible vision-based exam and documentation solution using a smartphone/tablet device, we conduct a comprehensive multi-test digitized neurological examination (DNE) dataset collection, namely DNE-113. Collected over 113 participants, DNE-113, a multi-test DNE database of finger tapping, finger to finger, forearm roll, stand-up and walk, and facial activation tests. Patients in DNE-113 were diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease (PD) or at least one other neurological (OD) disorder, based on their clinical record.
- Categories:
 788 Views
788 Views