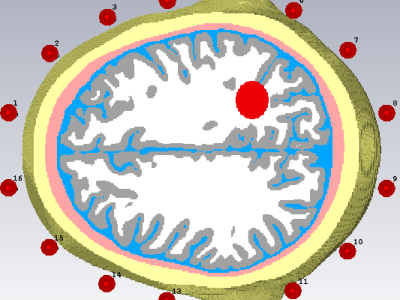
The proposed signals are used for electromagnetic-based stroke classification. Six realistic head phantom computed from MRI scans, is surrounded by an antenna array of 16 dipole antennas distributed uniformly around the head. These antennas are deployed in a fixed circular array around the head, at a distance of approximately 2-3 mm from the head.
- Categories: