Remote Sensing
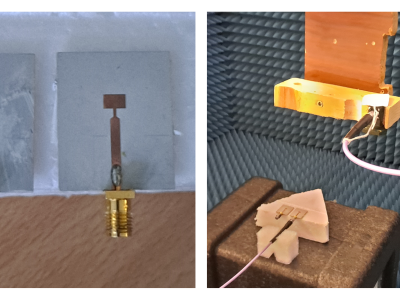
This dataset corresponds to the measurements of two microstrip patch antennas, collected using the facility described in [1]. The available measurements contained within the dataset allow a complete characterization of the field radiated by these antennas. These fields can be introduced in enhanced microwave imaging algorithms that consider the field radiated by the transmitting and receiving antennas of the microwave imaging system [2] (modified Delay and Sum algorithm), [3] (modified Phase Shift Migration imaging algorithm).
- Categories:
 158 Views
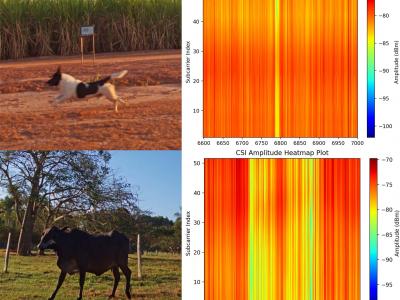
158 ViewsThis dataset is shared as part of the paper Towards scalable and low-cost WiFi sensing: preventing animal-vehicle collisions on rural roads, submitted to the IEEE Internet of Things Journal (IoT-J). It contains Wi-Fi Channel State Information (CSI) data from roadway crossings of small and large animals, persons and vehicles in rural environments.
- Categories:
 198 Views
198 Views
PU and PC datasets both were obtained through the reflective optics spectrographic Image system (ROSIS) sensors in Pavia, which is located in the northern region of Italy. The PU image has 610 × 315 pixels, 144 bands in the range of 430 - 860 nm, and 1.3-m spatial resolution. The PC image has 1906 × 715 pixels, 102 bands in the range of 430 - 860 nm, and 1.3-m spatial resolution. Both datasets include 9 distinct categories. Houston data was acquired over the University of Houston campus and its neighboring area on June 23, 2012.
- Categories:
 140 Views
140 ViewsSequences 1 and 2 are simulated from the satellite's perspective using CelesTrak data. Sequences 3 and 4 are real image sequences of asteroid 54. Sequences 1 and 2 each contain three targets, while sequences 3 and 4 each contain one target. Sequences 1 and 2 have a 2-degree field of view, 1s sampling interval, and targets with a $2\text{m}^2$ reflective area and 0.2 reflectivity. Sequences 3 and 4 were captured with a ground-based telescope (200 mm aperture, 1200 mm focal length, 0.86 arcseconds) and integration times of $2s$ and $3s$, respectively.
- Categories:
 144 Views
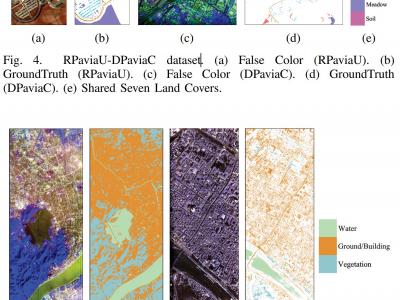
144 Views1) RPaviaU-DPaviaC Dataset: The RPaviaU-DPaviaC dataset is constructed by amalgamating two publicly accessible HSI datasets: the ROSIS Pavia University (RPaviaU) scene and the DAIS Pavia Center (DPaviaC) scene. The RPaviaU dataset, featuring dimensions of 610 × 340 × 103, was acquired by the ROSIS HSI sensor over the terrain of the University of Pavia, Italy. Conversely, the DPaviaC dataset, with dimensions of 400 × 400 × 72, was collected using the DAIS sensor over the central area of Pavia City, Italy. These two scenes share a common set of seven land cover classes.
- Categories:
 221 Views
221 ViewsBased on the analysis of laser characteristics, we have created a simulated dataset of near-infrared images of 1064nm laser spots. The spot collection process was carried out under natural light conditions. The divergence phenomenon during laser irradiation was excluded because the emitted 1064nm laser spots are adjustable.
- Categories:
 115 Views
115 Views
SECOND is a well-annotated benchmark for SCD. It collects bitemporal aerial images covering Hangzhou, Chengdu, Shanghai and other cities. The number of images totals 4662 pairs, of which 2968 pairs are used for training and 1694 pairs are used for testing. Each image has a size of 512 × 512 pixels with a spatial resolution from 0.5m to 3m. SENCOND provides unchanged masks and land cover masks in changed areas. It focuses on 6 common land cover classes, i.e., non-vegetated ground surface, tree, low vegetation, water, buildings and playgrounds.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 ViewsIn this dataset, a human detecting model using with UWB radar technology is presented. Two distinct datasets were created using the UWB radar device, leveraging its dual features. Data collection involved two main scenarios, each containing multiple sub-scenarios. These sub-scenarios varied parameters like the position, distance, angle, and orientation of the human subject relative to the radar. Unlike conventional approaches that rely on signal processing or noise/background removal, this study uniquely emphasizes analyzing raw UWB radar data directly.
- Categories:
 601 Views
601 Views
In this article, a novel method for interferometric target detection that employs coherent echoes and spatial frequency sampling is proposed. Originating from radio astronomy, interferometric passive microwave imaging has become widely applied for the passive microwave remote sensing of Earth. The proposed technique, termed Interferometric Coherent Echo Detection, is a novel active imaging method that capitalizes on coherent echoes to sample the spatial frequency domain.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views