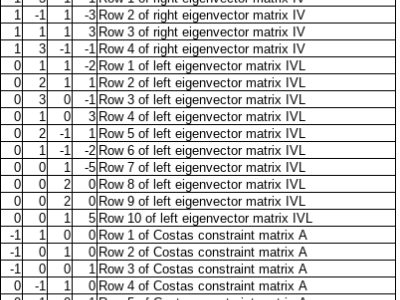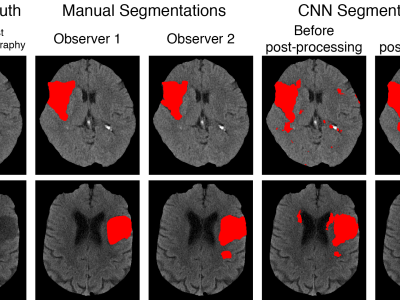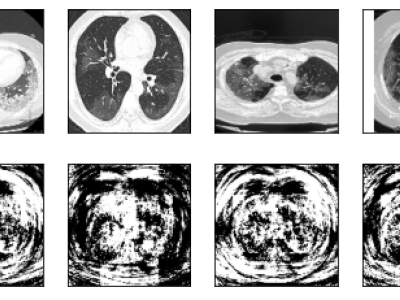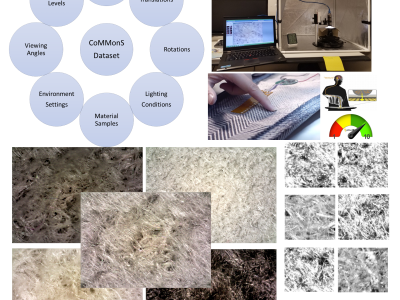
As one of the research directions at OLIVES Lab @ Georgia Tech, we focus on recognizing textures and materials in real-world images, which plays an important role in object recognition and scene understanding. Aiming at describing objects or scenes with more detailed information, we explore how to computationally characterize apparent or latent properties (e.g. surface smoothness) of materials, i.e., computational material characterization, which moves a step further beyond material recognition.
- Categories: