Signal Processing
In order to develop and analyse the performance of large-scale colored point cloud upsampling, we built a large-scale colored point cloud dataset for training and evaluating the upsampling network. This large-scale colored point cloud dataset consists of 121 original colored point clouds, 43 of which were scanned by us, while the other 78 were obtained from the SIAT-PCQD, Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) point cloud, and Greyc 3D colored mesh database. These point clouds cover six categories, including animals, plants, toys, sculptures, people and others.
- Categories:
 284 Views
284 ViewsBrain-Computer Interface (BCI) technology facilitates a direct connection between the brain and external devices by interpreting neural signals. It is critical to have datasets that contain patient's native languages while developing BCI-based solutions for neurological disorders. However, present BCI research lacks appropriate language-specific datasets, particularly for languages such as Telugu, which is spoken by more than 90 million people in India.
- Categories:
 452 Views
452 Views
This code implements a novel family of generalized exponentiated gradient (EG) updates derived from an Alpha-Beta divergence regularization function. Collectively referred to as EGAB, the proposed updates belong to the category of multiplicative gradient algorithms for positive data and demonstrate considerable flexibility by controlling iteration behavior and performance through three hyperparameters: alpha, beta, and the learning rate eta. To enforce a unit l1 norm constraint for nonnegative weight vectors within generalized EGAB algorithms, we develop two slightly distinct approaches.
- Categories:
 89 Views
89 ViewsIn this research, a small-scale drone with the required magnetometer sensor technologies and novel intelligent automated techniques -- Maggy, was built to automate and ease the procedures of cleaning landmines and UXO/IDE. The dataset with an MP4-formated video demonstrates how a magnetometer-integrated autonomous drone can map the magnetic field of a landmine region effectively and efficiently using an intelligent application through near real-time data streaming.
- Categories:
 228 Views
228 Views
Ten marine mammal calls and one ocean noise. The ten marine mammals are the ‘striped dolphin,’ ‘spinner dolphin,’ ‘spotted dolphin,’ ‘Ross's seal,’ ‘bearded seal,’ ‘killer whale,’ ‘sperm whale,’ ‘white whale,’ and ‘white whale. ‘Ross's seal, bearded seal, killer whale, sperm whale, beluga whale, and pilot whale. ’, ‘pilot whale’ and ‘pilot whale’.' ‘sperm whale’, ‘beluga whale’, ‘pilot whale’ and ‘humpback whale’.We used the recording data of ten marine mammals from 1940 to 2000 provided by the Watkins Marine Mammal Sound Library.
- Categories:
 293 Views
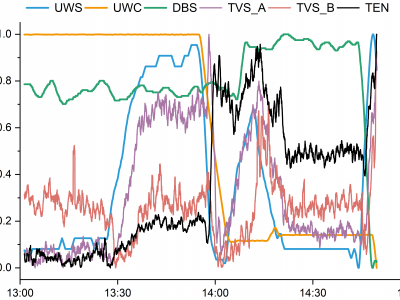
293 ViewsThis graph illustrates the visualization trend of a subset of the dataset I have uploaded, which comprises 6500*9 data points. The dataset consists of nine columns representing underwater speed (UWS), underwater course (UWC), depth below the surface (DBS), rate of change in speed (RCS), rate of change in course (RCC), rate of change in depth (RCD), trend A and B of vibrational signals (TVS_A, TVS_B) and electromagnetic noise trend (TEN) recorded by the AUV.
- Categories:
 140 Views
140 Views
Dataset containing real word data related to the informations receive on a downlink and an uplink channels. The information related to the data flowing on the channel are expressed by means of complex numbers. Some processing can be performed to convert the complex number into integer numbers in order to represent the channel as preferred. This dataset can be used to develop new compression and channel estimation algorithms.
- Categories:
 426 Views
426 ViewsRLED contains 80,400 images and corresponding events, we utilized a photometer to continuously measure scene illumination and calculate the illumination value after attenuation at the event camera. The capture scenes included city (35.0%), suburbs (10.3%), town (14.5%), village (17.8%), and valley (22.4%). Half of the RLED frames are captured at a frame rate of 25 fps, and the other half at 10 fps. The exposure time is set to 1ms, 3ms, and 5ms based on the varying environmental illumination.
- Categories:
 209 Views
209 ViewsAbstract—In massive Internet of Things (IoT) deployments,
the efficient allocation of computing resources to IoT devices
while preserving devices’ data poses a significant challenge.
This paper proposes a new online probabilistic model to address
uncertainties in demand and resource allocation for IoT
networks, where the task computing of requesting devices is
addressed by serving devices. The model incorporates uncertainty
and formulates an optimization problem, concerning available
- Categories:
 149 Views
149 Views