Machine Learning
Wine has been popular with the public for centuries; in the market, there are a variety of wines to choose from. Among all, Bordeaux, France, is considered as the most famous wine region in the world. In this paper, we try to understand Bordeaux wines made in the 21st century through Wineinformatics study. We developed and studied two datasets: the first dataset is all the Bordeaux wine from 2000 to 2016; and the second one is all wines listed in a famous collection of Bordeaux wines, 1855 Bordeaux Wine Official Classification, from 2000 to 2016.
- Categories:
 2233 Views
2233 Views
Intending to cover the existing gap regarding behavioral datasets modelling interactions of users with individual a multiple devices in Smart Office to later authenticate them continuously, we publish the following collection of datasets, which has been generated after having five users interacting for 60 days with their personal computer and mobile devices. Below you can find a brief description of each dataset.
- Categories:
 545 Views
545 ViewsStable and efficient walking strategies for humanoid robots usually relies on assumptions regarding terrain characteristics. If the robot is able to classify the ground type at the footstep moment, it is possible to take preventive actions to avoid falls and to reduce energy consumption.
This dataset contains raw data from 10 inertial and torque sensors of a humanoid robot, sampled after the impact between foot and ground. There are two types of data: simulated using gazebo and data from a real robot.
- Categories:
 563 Views
563 ViewsWhile social media has been proved as an exceptionally useful tool to interact with other people and massively and quickly spread helpful information, its great potential has been ill-intentionally leveraged as well to distort political elections and manipulate constituents. In the paper at hand, we analyzed the presence and behavior of social bots on Twitter in the context of the November 2019 Spanish general election.
- Categories:
 1653 Views
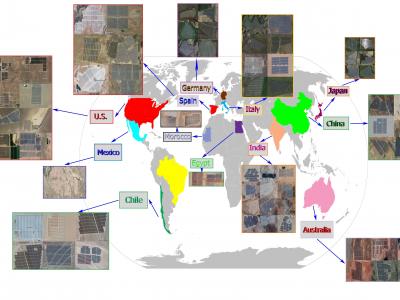
1653 ViewsExtracting the boundaries of Photovoltaic (PV) plants is essential in the process of aerial inspection and autonomous monitoring by aerial robots. This method provides a clear delineation of the utility-scale PV plants’ boundaries for PV developers, Operation and Maintenance (O&M) service providers for use in aerial photogrammetry, flight mapping, and path planning during the autonomous monitoring of PV plants.
- Categories:
 1434 Views
1434 ViewsThis work develops a novel power control framework for energy-efficient powercontrol in wireless networks. The proposed method is a new branch-and-boundprocedure based on problem-specific bounds for energy-efficiency maximizationthat allow for faster convergence. This enables to find the global solution forall of the most common energy-efficient power control problems with acomplexity that, although still exponential in the number of variables, is muchlower than other available global optimization frameworks.
- Categories:
 472 Views
472 Views
Normal
0
7.8 磅
0
2
false
false
false
EN-US
ZH-CN
X-NONE
- Categories:
 181 Views
181 ViewsThis dataset is composed of 4-Dimensional time series files, representing the movements of all 38 participants during a novel control task. In the ‘5D_Data_Extractor.py’ file this can be set up to 6-Dimension, by the ‘fields_included’ variable. Two folders are included, one ready for preprocessing (‘subjects raw’) and the other already preprocessed ‘subjects preprocessed’.
- Categories:
 317 Views
317 Views
The ship motion data collected in this paper is actually measured when the ship is sailing at sea. The heave displacement is measured by a laser ranging sensor. The roll and pitch angles are collected by an electronic inclinometer. The sampling time of the data set exceeds 1000s, the collection interval is 0.176s, the collection frequency is 6 times per second, and there are more than 6000 sets of data in total.
- Categories:
 1146 Views
1146 Views
We develop a general group-based continuous-time Markov epidemic model (GgroupEM) framework for any compartmental epidemic model (e.g., susceptible-infected-susceptible, susceptible-infected-recovered, susceptible-exposed-infected-recovered). Here, a group consists of a collection of individual nodes of a network. This model can be used to understand the critical dynamic characteristics of a stochastic epidemic spreading over large complex networks while being informative about the state of groups.
- Categories:
 205 Views
205 Views