Artificial Intelligence
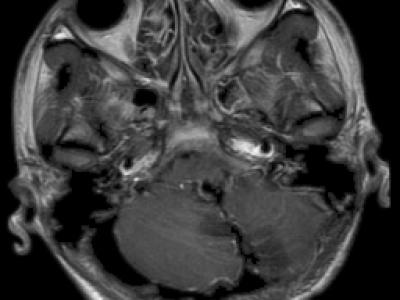
本文介绍了一种无人监督的医疗 旨在解决高斯-泊松挑战的图像去噪模型 CT、MRI 和 X 射线图像中的混合噪声。传统深度图像先验 (DIP) 使用随机噪声作为网络输入的方法收敛缓慢, 而直接使用观察到的噪点图像通常会导致过度拟合和较差 去噪性能。为了克服这些限制,我们将 frequency 和 用于对观察到的噪声进行多通道处理的空间域信息 图像。然后,特征融合模块集成了两个域的优势, 能够更准确地提取结构信息,显著 提高降噪性能,并加速收敛。此外,我们 引入基于熵的提前停止机制,用于动态监控 训练期间熵的变化,自动停止迭代一次 熵减少并稳定,从而防止过拟合。此外 该模型采用 L1 损失函数,而不是使用的传统 MSE 损失 以更好地保留图像边缘和细节。实验结果表明 所提出的模型具有优势,PSNR 平均增加 10.7%,并且 与 DIP 相比,SSIM 为 17.9%。值得注意的是,到第 60 次迭代时,PSNR 和 所提出的方法的 SSIM 值已经超过了峰值 在第 1,360 次迭代中通过 DIP 实现,在第 2,600 次迭代中由 DIP 变体实现 迭 代。所提出的模型提供了一种高效、稳健和创新的方法 医学影像降噪任务的解决方案。
- Categories:
 203 Views
203 ViewsTraditional magnetic localization methods based on mathematical model and optimization algorithm often fail to achieve the global optimum due to their dependency on initial values of pose parameters. Despite deep learning can potentially address these limitations, the existing methods are restricted to capture both global position distribution and local spatial features, leading to diminished performance in tasks required precise pose information.
- Categories:
 61 Views
61 Views
The softwarization and virtualization of the fifth-generation (5G) cellular networks bring about increased flexibility and faster deployment of new services. However, these advancements also introduce new vulnerabilities and unprecedented attack surfaces. The cloud-native nature of 5G networks mandates detecting and protecting against threats and intrusions in the cloud systems.
- Categories:
 196 Views
196 ViewsThe advancement and ubiquity of digital networks have fundamentally transformed numerous spheres of human activity. At the heart of this phenomenon lies the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) model, whose influence is particularly notable in the exponential growth of the Internet due to its potential ability to transmit flexibly through an advanced Congestion Control (CC). Seeking an even more efficient CC mechanism, this work proposes the construction of Deep Learning Neural Networks (MLP, LSTM, and CNN) for classifying network congestion levels.
- Categories:
 152 Views
152 ViewsThe data used in this work is collected using the AirBox Sense system developed to detect six air pollutants, ambient temperature, and ambient relative humidity. The pollutants are Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2), surface Ozone (O3), Carbon Monoxide (CO), Sulphur Dioxide (SO2), Particulate Matter (PM2.5, and PM10). The sensors monitor these pollutants in real-time and store them in a cloud-based platform using a cellular module. Data are collected every 20 seconds, producing 4320 readings each day.
- Categories:
 213 Views
213 ViewsScene understanding is essential for a wide range of robotic tasks, such as grasping. Simplifying the scene into predefined forms makes the robot perform the robotic task more properly, especially in an unknown environment. This paper proposes a combination of simulation-based and realworld datasets for domain adaptation purposes and grasping in practical settings. In order to compensate for the weakness of depth images in previous studies reported in the literature for clearly representing boundaries, the RGB image has also been fed as input in RGB and RGB-D input modalities.
- Categories:
 351 Views
351 ViewsThis work presents a specialized dataset designed to advance autonomous navigation in hiking trail and off-road natural environments. The dataset comprises over 1,250 images (640x360 pixels) captured using a camera mounted on a tele-operated robot on hiking trails. Images are manually labeled into eight terrain classes: grass, rock, trail, root, structure, tree trunk, vegetation, and rough trail. The dataset is provided in its original form without augmentations or resizing, allowing end-users flexibility in preprocessing.
- Categories:
 507 Views
507 ViewsThis dataset, titled "Synthetic Sand Boil Dataset for Levee Monitoring: Generated Using DreamBooth Diffusion Models," provides a comprehensive collection of synthetic images designed to facilitate the study and development of semantic segmentation models for sand boil detection in levee systems. Sand boils, a critical factor in levee integrity, pose significant risks during floods, necessitating accurate and efficient monitoring solutions.
- Categories:
 287 Views
287 Views
The UNISTUDIUM dataset contains the logs collected by Unistudium, the University of Perugia elearning platform based on moodle, a open source software for learning management systems (https://moodle.org).
The collected logs record interactions with the platform of students attending 4 courses during the time period of one semester, from 1st September to 31st December.
- Categories:
 150 Views
150 ViewsWe organized and collected two years' worth of complete fault work orders from a wind farm, and structured these work orders into a fault diagnosis event knowledge graph using the proposed algorithm. This graph includes fault modes, fault impacts, fault symptoms, inspection schemes, root cause identification, and maintenance strategies, covering all potential fault information and handling methods for wind turbines. This dataset records the head entity-relation-tail entity information in the form of triples using JSON format.
- Categories:
 746 Views
746 Views