Wearable Sensing
This study examined the effectiveness of a detection-based lie detection method that determines lying conditions based on facial autonomic reactions. This technique combines with two other lie detection techniques using a multi sensor fusion technique that is used in the polygraph test to differentiate moments of participants lying and telling the truth about a picked-up card from a deck of cards. Experiments were conducted with 19 participants sitting in front of a camera connected to Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) probes and ECG probes for a polygraph test.
- Categories:
 1785 Views
1785 Views
Training data of Human Motion Recognition via Wearable plastic Fiber Sensing System
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
Anatomical landmark trajectories are commonly used to define joint coordinate systems in human kinematic analysis according to standards proposed by the International Society of Biomechanics (ISB). However, most inertial motion capture (IMC) studies focus only on joint angle measurement, which limits its application. Therefore, this paper proposes a new method to calculate the trajectories of anatomical landmarks based on IMC data. The accuracy and reliability of this method were investigated by comparative analysis based on measurement data from 16 volunteers.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
10 soccer supporters gathered to watch a live broadcasted Premier League
match between Liverpool and Manchester United (4 - 0) on 19th of March 2022, all
equipped with wrist-worn accelerometers. All participants were aware of the purpose of this experiment and consented to participate
by attendance at the event, and by wearing the accelerometer. No personally sensitive
information was collected, all data is fully anonymised following the GDPR guidelines
and all procedures were in accordance with the recommendations of the data protection
- Categories:
 150 Views
150 Views
Grasp intention recognition is a vital problem for controlling assistive robots to help the elderly and infirm people restore arm and hand function. This dataset contains gaze data and scene image data of healthy individuals and hemiplegic patients while performing different grasping tasks. It can be used for gaze-based grasp intention recognition studies.
- Categories:
 199 Views
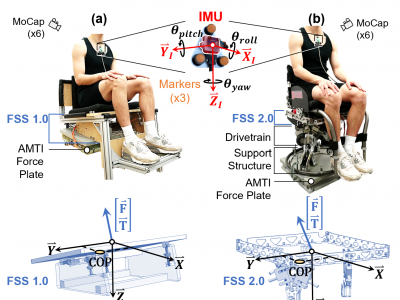
199 ViewsThis data was collected during a validation study of our Torso-Dynamics Estimation System (TES). The TES consisted of a Force Sensing Seat (FSS) and an inertial measurement unit (IMU) that measured the kinetics and kinematics of the subject's torso motions. The FSS estimated the 3D forces, 3D moments, and 2D COPs while the IMU estimated the 3D torso angles. To validate the TES, the FSS and IMU estimates were compared to gold standard research equipment (AMTI force plate and Qualisys motion capture system, respectively).
- Categories:
 121 Views
121 ViewsThe dataset contains pressure insole data from twenty subjects who performed five tasks, comprising of two common daily activities (standing and walking), and three industry-focussed tasks (manual handling, assembly and pick and place). The speed and order in which a given task was completed was not prescribed. The data pertains to the areas of human factors, ergonomics and occupational health and safety research, among others, and enables an understanding of the force distributions involved in common tasks as well as physical and manufacturing type tasks.
- Categories:
 76 Views
76 ViewsIREYE4TASK is a dataset for wearable eye landmark detection and mental state analysis. Sensing the mental state induced by different task contexts, where cognition is a focus, is as important as sensing the affective state where emotion is induced in the foreground of consciousness, because completing tasks is part of every waking moment of life. However, few datasets are publicly available to advance mental state analysis, especially those using the eye as the sensing modality with detailed ground truth for eye behaviors.
- Categories:
 1031 Views
1031 Views