Datasets
Standard Dataset
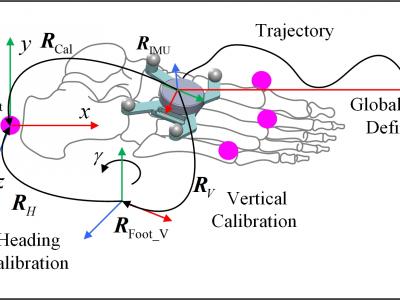
A Method for Calculating Lower Extremity Anatomical Landmark Trajectories Based on Inertial Motion Capture Data

- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Zhengtao Wang
- Last updated:
- Mon, 07/08/2024 - 15:58
- DOI:
- 10.21227/7sft-wj45
- License:
 14 Views
14 Views- Categories:
Abstract
Anatomical landmark trajectories are commonly used to define joint coordinate systems in human kinematic analysis according to standards proposed by the International Society of Biomechanics (ISB). However, most inertial motion capture (IMC) studies focus only on joint angle measurement, which limits its application. Therefore, this paper proposes a new method to calculate the trajectories of anatomical landmarks based on IMC data. The accuracy and reliability of this method were investigated by comparative analysis based on measurement data from 16 volunteers. The results showed that the accuracy of anatomical landmark trajectories was 23.4 to 57.3mm, about 5.9% to 7.6% of the segment length, the orientation accuracy was about 3.3° to 8.1°, less than 8.6% of the range of motion (ROM),using optical motion capture results as the gold standard.
All data processing was done in MATLAB 2022a. Run Main.mlx.
We use btk toolkit download from http://biomechanical-toolkit.github.io/docs/Wrapping/Matlab/index.html
More from this Author