Datasets
Standard Dataset
An ultrasound brain dataset for foreign body detection in neurosurgery
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Avisha Kumar
- Last updated:
- Fri, 01/03/2025 - 09:55
- DOI:
- 10.21227/v4y4-k985
- Data Format:
- License:
 144 Views
144 Views- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
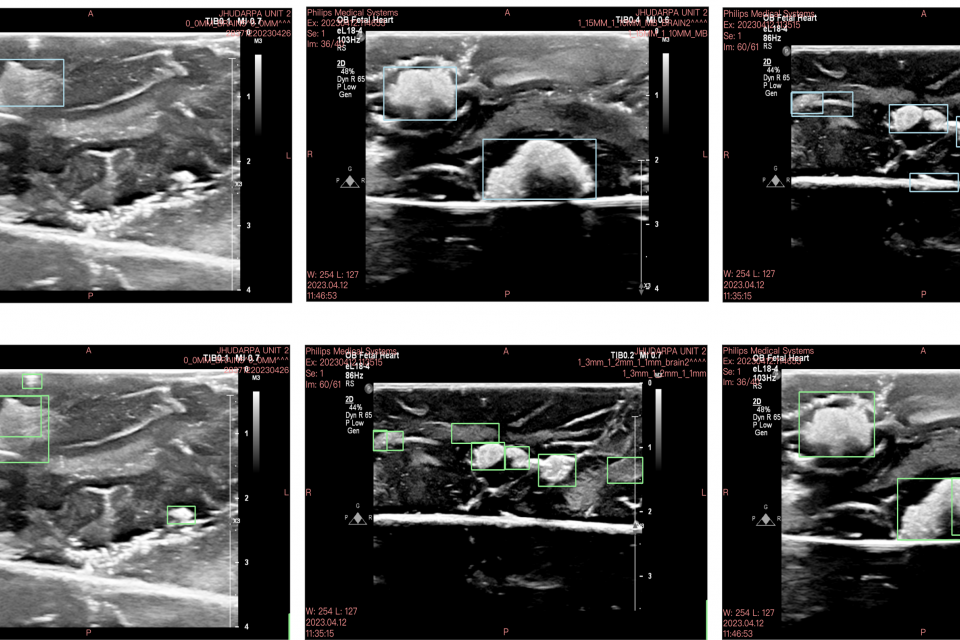
The removal of surgical tools from the brain is a critical aspect of post-operative care. Surgical sponges such as cotton balls are one of the most commonly retained tools, as they become visually indistinguishable from the surrounding brain tissue when soaked with blood and can fragment into smaller pieces. This can lead to life-threatening immunological responses and invasive reoperation, demonstrating the need for new foreign body object detection methods. Ultrasound imaging, which differentiates between the acoustic properties of cotton and brain tissue, can provide a method for visually detecting these objects intraoperativley. Advances in deep learning and computer vision models have demonstrated the ability for automated object detection from ultrasound images, but these models require large amounts of training data and are often trained on privately developed datasets. In this study, we present a novel ultrasound data resource to train deep learning algorithms for clinical translation in the brain. The dataset is comprised of 860 annotated ultrasound images of ex vivo porcine brains containing cotton balls of varying sizes and amounts. State-of-the-art deep learning models were then evaluated on the dataset, and our results show that YOLOv9 achieves the highest accuracy out of all tested models with a mean Average Precision (mAP50-95) of 0.657. Our publicly available dataset provides a robust resource for researchers to further enhance object detection tools in neurosurgery.
The dataset contains all 860 images and associated annotations in both xml and txt format. The three main folders are the images folder, xml labels folder, and txt labels folder. In each of these folders it is split into train, validation, test folders.