Computer Vision
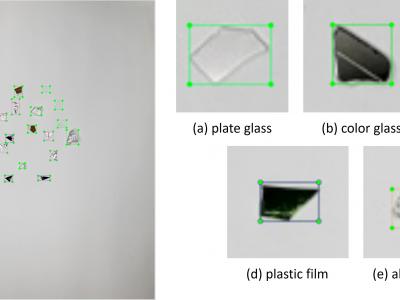
This dataset was collected from real-world recycling plants, primarily consisting of crushed glass from disassembled display devices. The dataset contains images of flat glass mixed with solid glass, colored glass, plastic film, and aluminum foil. The colored glass originated from frame areas, while the aluminum foil came from cable shielding materials. Additional objects, such as solid glass and plastic films, were sourced from other recycled materials like glass bottles and packaging.
- Categories:
 160 Views
160 Views
- Categories:
 648 Views
648 ViewsCrackAirport features images containing unique elements such as aircraft, T-hangars, vegetation, airport markings and signs, as well as evidence of previous maintenance. The dataset was captured using a Sony ILCE-7RM4A camera mounted on a drone flying at an altitude of 100 feet AGL. The imagery was sourced from various local airports in Tennessee and includes common pavement distresses and environmental patterns typical of airport surfaces. The images were annotated and then cropped into 512x512 pixel segments for training.
- Categories:
 799 Views
799 ViewsThe ultrasound video data were collected from two sets of neck ultrasound videos of ten healthy subjects at the Ultrasound Department of Longhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Each subject included video files of two groups of LSCM, LSSCap, RSCM, and RSSCap. The video format is avi.
The MRI training data were sourced from three hospitals: Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Huadong Hospital, Fudan University; and Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital.
- Categories:
 579 Views
579 ViewsThese are tight pedestrian masks for the thermal images present in the KAIST Multispectral pedestrian dataset, available at https://soonminhwang.github.io/rgbt-ped-detection/
Both the thermal images themselves as well as the original annotations are a part of the parent dataset. Using the annotation files provided by the authors, we develop the binary segmentation masks for the pedestrians, using the Segment Anything Model from Meta.
- Categories:
 650 Views
650 Views
The Dataset is a large-scale, diverse collection of high-resolution RGB images containing labeled wheat heads. Assembled through a collaborative effort of nine research institutes from seven countries, the dataset encompasses a wide range of genotypes, growth stages, and pedoclimatic conditions. Its primary goal is to facilitate the development of robust and accurate wheat head detection models for applications in precision phenotyping and crop management.
- Categories:
 199 Views
199 ViewsWe introduce two novel datasets for cell motility and wound healing research: the Wound Healing Assay Dataset (WHAD) and the Cell Adhesion and Motility Assay Dataset (CAMAD). WHAD comprises time-lapse phase-contrast images of wound healing assays using genetically modified MCF10A and MCF7 cells, while CAMAD includes MDA-MB-231 and RAW264.7 cells cultured on various substrates. These datasets offer diverse experimental conditions, comprehensive annotations, and high-quality imaging data, addressing gaps in existing resources.
- Categories:
 1047 Views
1047 Views
Video anomaly detection (VAD) is a challenging task aiming to recognize anomalies in video frames, and existing large-scale VAD researches primarily focus on road traffic and human activity scenes. In industrial scenes, there are often a variety of unpredictable anomalies, and the VAD method can play a significant role in these scenarios. However, there is a lack of applicable datasets and methods specifically tailored for industrial production scenarios due to concerns regarding privacy and security.
- Categories:
 324 Views
324 ViewsThe burgeoning demand for collaborative robotic systems to execute complex tasks collectively has intensified the research community's focus on advancing simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) in a cooperative context. Despite this interest, the scalability and diversity of existing datasets for collaborative trajectories remain limited, especially in scenarios with constrained perspectives where the generalization capabilities of Collaborative SLAM (C-SLAM) are critical for the feasibility of multi-agent missions.
- Categories:
 387 Views
387 Views
Perception systems are vital for the safety of autonomous driving. In complex autonomous driving scenarios, autonomous vehicles must overcome various natural hazards, such as heavy rain or raindrops on the camera lens. Therefore, it is essential to conduct comprehensive testing of the perception systems in autonomous vehicles against these hazards, as demanded by regulatory agency of many countries for human drivers.
- Categories:
 299 Views
299 Views