*.csv (zip)
DevicePure.com is the large free repository for device specifications website, with the Manuals, Documents of devices, and applications available on the Internet.
It provides Samsung Firmware update for all Samsung smartphone devices. The database includes over 60.000 firmware update information of Samsung and describes updates with 79 languages.
- Categories:
 819 Views
819 ViewsIndustrial Internet of Things (IIoTs) are high-value cyber targets due to the nature of the devices and connectivity protocols they deploy. They are easy to compromise and, as they are connected on a large scale with high-value data content, the compromise of any single device can extend to the whole system and disrupt critical functions. There are various security solutions that detect and mitigate intrusions.
- Categories:
 5594 Views
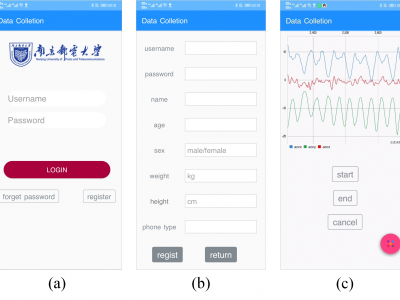
5594 ViewsDataset I mainly consists of 30 subjects, which are respectively composed of gait data collected by mobile phone placed on arm, wrist, hand, waist, and ankle. This dataset is used to verify the impact of the mobile phone's placement on the recognition effect. Dataset II and Dataset III are composed of 113 subjects. Dataset II is the data collected from a mobile phone placed in the hand position, while Dataset III is the gait data collected from a mobile phone placed in the waist position. These two data sets are used primarily to verify the identification effect of the proposed model.
- Categories:
 492 Views
492 ViewsThe AOLAH databases are contributions from Aswan faculty of engineering to help researchers in the field of online handwriting recognition to build a powerful system to recognize Arabic handwritten script. AOLAH stands for Aswan On-Line Arabic Handwritten where “Aswan” is the small beautiful city located at the south of Egypt, “On-Line” means that the databases are collected the same time as they are written, “Arabic” cause these databases are just collected for Arabic characters, and “Handwritten” written by the natural human hand.
- Categories:
 1046 Views
1046 ViewsThe dataset consists of 751 videos, each containing the performance one of the handball actions out of 7 categories (passing, shooting, jump-shot, dribbling, running, crossing, defence). The videos were manually extracted from longer videos recorded in handball practice sessions.
- Categories:
 1336 Views
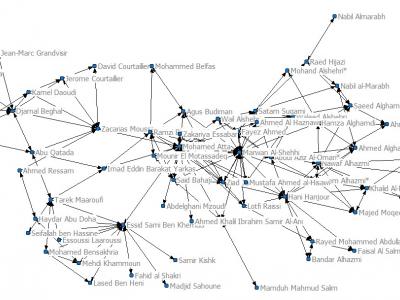
1336 Views· 9/11 hijackers network dataset [20]: The 9/11 hijackers network incorporates 61 nodes (each node is a terrorist involved in 9/11 bombing at World Trade Centers in 2011). Dataset was prepared based on some news report, and ties range from ‘at school with’ to ‘on the same plane’. The Data consists of a mode matrix with 19*19 terrorist by terrorist having trusted prior contacts with 1 mode matrix of 61 edges of other involved associates.
- Categories:
 1129 Views
1129 Views
The datasets in the compressed file were used in the case study of the article entitled Automated Machine Learning Pipeline for Geochemical Analysis by Germán H. Alférez, et al. Our approach was evaluated with a compositional dataset from 6 fault-separated blocks in the Peninsular Ranges Province and Transverse Ranges Province. The Peninsular Ranges are a group of mountain ranges, stretching from Southern California to Southern Baja California, Mexico. North of the Peninsular Ranges Province is the east-west Transverse Ranges Province.
- Categories:
 322 Views
322 Views