Agriculture
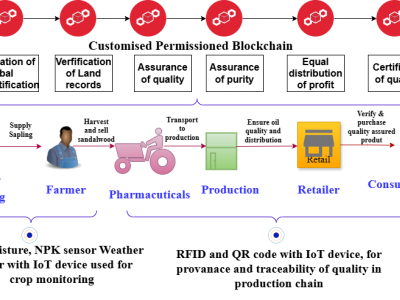
The incorporation of Internet of Things (IoT) technology with agriculture has transformed several farming practices, bringing unparalleled simplicity and efficiency. This article explores the robust integration of IoT and blockchain technology(BIoT) in agricultural operations, offering insight into the resulting BIoT system’s design. This study investigates the potential benefits of merging the IoT and blockchain technologies in agriculture. A system for tracking plant growth using sensors and blockchain-integrated IoT has been developed and analyzed.
- Categories:
 138 Views
138 ViewsWith the gradual maturity of UAV technology, it can provide extremely powerful support for smart agriculture and precise monitoring. Currently, there is no dataset related to green walnuts in the field of agricultural computer vision. Therefore, in order to promote the algorithm design in the field of agricultural computer vision, we used UAV to collect remote sensing data from 8 walnut sample plots.
- Categories:
 202 Views
202 Views
The PlantVillage dataset, with over 54,000 images spanning 14 plant species and 26 disease types, has been widely used for leaf disease classification. However, it is limited in both scale and diversity. To address these limitations, we developed LeafNet, a large-scale dataset designed to support foundation models for leaf disease diagnosis. LeafNet comprises over 186,000 images from 22 crop species, covering 43 fungal diseases, 8 bacterial diseases, 2 mould (oomycete) diseases, 6 viral diseases, and 3 mite-induced diseases, categorized into 97 classes.
- Categories:
 274 Views
274 Views
This is a dataset containing images of cotton leaves with Verticillium wilt, brown spot, aphids, and healthy leaves.The dataset initially consisted of original images of brown spot disease (330 images), verticillium wilt (213 images), healthy leaves (383 images), and aphids (473 images). To balance class distributions and improve model performance, data augmentation techniques such as flipping and scaling were applied.
- Categories:
 195 Views
195 Views
This dataset includes spectra of 250 corn samples with different vitality levels, with a data size of 250*256, categorized into five vitality grades. The imaging spectrometer employs a series spectrophotometer, model N17E, with a spectral range of 874-1734nm and a spectral resolution of 5nm. The CCD used is model ICL-B1410, featuring 1600×1200 pixels, and is equipped with an OLES22 lens with a focal length of 22mm.
- Categories:
 126 Views
126 ViewsRipe and unripe pistachios lies in their appearance, taste, and texture, as well as their uses. Ripe Pistachio: The kernel inside is vibrant green with purple skin, larger, and fully developed. More aromatic and flavorful than unripe pistachios. Widely used in desserts (ice creams, baklava, pastries) and savory dishes. Unripe Pistachio: The nut kernel is smaller and pale green or yellowish. Less sweet and not as flavorful as ripe pistachios. Sometimes used in specialty cuisines, pickling, or as a garnish. This dataset contains 966 images for ripe and 966 images for unripe classes.
- Categories:
 284 Views
284 ViewsSatellite image crop classification utilizes remote sensing technology for efficient monitoring and analysis of agricultural land. By acquiring satellite data at different times and spectral bands, the spectral characteristics of crops can be extracted to identify different crop types. In recent years, with the development of machine learning and deep learning algorithms, classification accuracy has significantly improved.
- Categories:
 152 Views
152 Views
The IP102 dataset comprises 75,222 images of 102 pest species, out of which 12 classes are chosen for detection tasks. The custom pest dataset contains 10 categories of pests commonly found in crops like rice, maize, soybean, and canola. It includes images captured under varied real-world conditions, such as different lighting, occlusion, and complex backgrounds, making it highly representative of practical agricultural scenarios.
- Categories:
 173 Views
173 Views
With the increase in world population, agricultural planning is significant to ensure food security. Timely recommendations for crops could be valuable for planning food production and maintaining food sustainability. This proposed work suggests a crop recommendation model considering physical soil characteristics, chemical soil characteristics, climate, and crop characteristics, using Improved Deep Belief Networks (IDBN). For this study, four important Indian crops—rice, maize, finger millet and sugarcane were taken into account.
- Categories:
 327 Views
327 Views