Artificial Intelligence

The NYUD V2 data set is comprised of video sequences from a variety of indoor scenes as recorded by both the RGB and Depth cameras from the Microsoft Kinect. It features: 1449 densely labeled pairs of aligned RGB and depth images 464 new scenes taken from 3 cities, 407,024 new unlabeled frames
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 ViewsTo generate the training and validation datasets, the fullwave electromagnetic solver FEKO is utilized. The phase of the reference antenna (Antenna 1) is fixed at 0°, while the phases of the other three antennas are varied in 30° steps within the range [0◦ , 360◦ ]. This results in 13×13×13 = 2197 distinct phase combinations. For each combination, the farfield radiation intensities are extracted on the XOY, YOZ, and XOZ planes, yielding a total of 2197 × 3 data samples. For testing, 343 new phase combinations are generated within the interval [15◦ , 195◦ ] using 30° steps (i.e., 7×7×7).
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 ViewsTo generate the training and validation datasets, the fullwave electromagnetic solver FEKO is utilized. The phase of the reference antenna (Antenna 1) is fixed at 0°, while the phases of the other three antennas are varied in 30° steps within the range [0◦ , 360◦ ]. This results in 13×13×13 = 2197 distinct phase combinations. For each combination, the farfield radiation intensities are extracted on the XOY, YOZ, and XOZ planes, yielding a total of 2197 × 3 data samples. For testing, 343 new phase combinations are generated within the interval [15◦ , 195◦ ] using 30° steps (i.e., 7×7×7).
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
This dataset comprises vibration signals collected from bearing test rigs under both healthy and faulty conditions, designed to support research in fault diagnosis and out-of-distribution (OOD) detection. The data includes:
-
CWRU Dataset: Signals from the Case Western Reserve University bearing test platform, sampled at 12 kHz, covering normal operation and three fault types (inner race, outer race, and rolling element faults) with varying severities (0.007–0.021 inches). OOD samples are explicitly labeled for validation.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
Vertical Federated Learning (VFL) enables multiple organizations to collaboratively train machine learning models without sharing raw data, particularly suited for tabular datasets with aligned sample IDs but disjoint feature spaces. Despite its growing relevance in privacy-sensitive sectors such as finance and healthcare, publicly available benchmarks for VFL on tabular data remain limited. This paper introduces and categorizes a collection of real-world tabular datasets tailored for VFL research, highlighting their feature distribution, domain applicability, and security relevance.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
Paper : Assessment of Inference Improvements for Facial Micronutrient Deficiency Detection using Attention-Enhanced YOLOv5
Authors : Amey Agarwal, Shreya Rathod, Riva Rodrigues, Nirmitee Sarode, Dhananjay R. Kalbande
Desciption
This is a dataset of 7 classes : 6 facial skin problems and 1 null class.
A facial skin problem may be identified in an image and marked using Bounding Box Annotation.
Acne Class indicates deficiency of Vitamin D
Blackhead and Nodules are types of acne
- Categories:
 9 Views
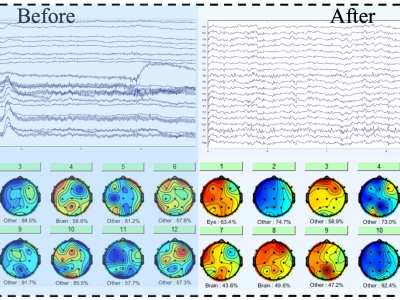
9 ViewsThis repository contains resources for EEG data processing and cognitive load recognition using a Multi-Head Attention EEGNet model. It includes original EEG data, MATLAB code for preprocessing, and Python code for classification.
With the ethics approval obtained from our institution, this study acquired 30 subjects aged between 18 to 29 to conduct research. Informed written consents were attained from all participants. The selection of participants follows a standardized and rigorous protocol that they have to meet the following requirements:
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views
We present TriviaQA, a challenging reading comprehension dataset containing over 650K question-answer-evidence triples. TriviaQA includes 95K question-answer pairs authored by trivia enthusiasts and independently gathered evidence documents, six per question on average, that provide high quality distant supervision for answering the questions.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
Large Language Models (LLMs) have been widely used to automate programming tasks. Their capabilities have been evaluated by assessing the quality of generated code through tests or proofs. The extent to which they can reason about code is a critical question revealing important insights about their true capabilities. This paper introduces CodeMind, a framework designed to gauge the code reasoning abilities of LLMs through the following explicit and implicit code reasoning tasks: Independent Execution Reasoning (IER), Specification Reasoning (SR) and Dynamic Semantics Reasoning (DSR).
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views