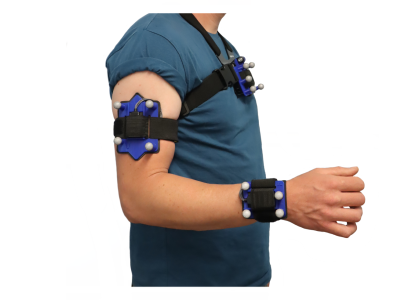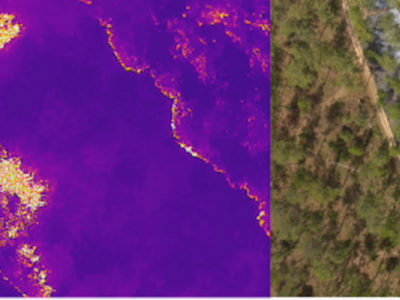
FLAME 3 is the third dataset in the FLAME series of aerial UAV-collected side-by-side multi-spectral wildlands fire imagery (see FLAME 1 and FLAME 2). This set contains a single-burn subset of the larger FLAME 3 dataset focusing specifically on Computer Vision tasks such as fire detection and segmentation.
- Categories: