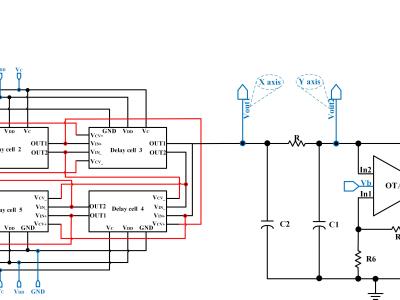
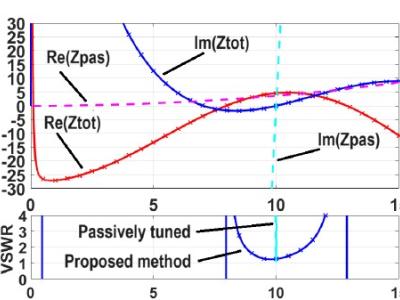
A comparator is used to compare two voltages and produce a digital output signal based on the comparison result. Filters, on the other hand, are designed to allow certain frequencies to pass while attenuating others. During testing, for comparators, parameters such as hysteresis and response time are measured. For filters, characteristics like cutoff frequency, roll-off rate, and attenuation in the stopband are evaluated.
- Categories: