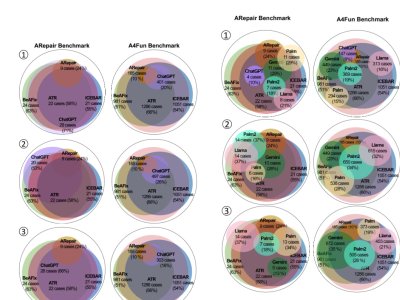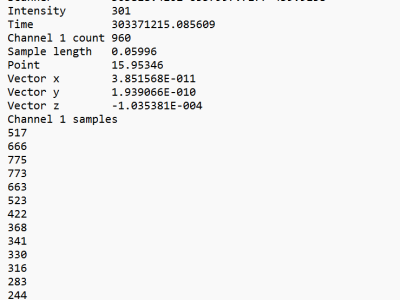
The dataset used in this study consists of Airborne LiDAR Bathymetry (ALB) waveform data collected by the Norwegian Mapping Authority via Field Geospatial AS. It covers the Fjøløy Island area in Stavanger, Norway, a region characterized by fjords and diverse submerged environments. The dataset is proprietary and was provided to the authors under a research collaboration agreement.
Two subsets were extracted from the full dataset:
- Dataset 1: 6,379 waveform files
- Dataset 2: 4,428 waveform files
Each waveform file contains:
- Categories: