Automated Repair of Declarative Software Specifications in the Era of Large Language Models
- Citation Author(s):
-
Jiawei Li (University of California, Irvine)
- Submitted by:
- Md Rashedul Hasan
- Last updated:
- DOI:
- 10.21227/yt7g-bk72
- Data Format:
- Links:
 234 views
234 views
- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
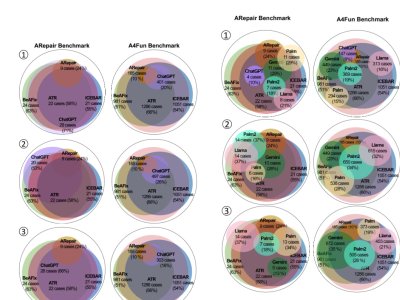
The growing adoption of declarative software specification languages, coupled with their inherent difficulty in debugging, has underscored the need for effective and automated repair techniques applicable to such languages. Researchers have recently explored various methods to automatically repair declarative software specifications, such as template-based repair, feedback-driven iterative repair, and bounded exhaustive approaches. The latest developments in Large Language Models (LLMs) provide new opportunities for the automatic repair of declarative specifications. In this study, we assess the effectiveness of utilizing different LLMs to repair software specifications written in the Alloy declarative language. Unlike imperative languages, specifications in Alloy are not executed but rather translated into logical formulas and evaluated using backend constraint solvers to identify specification instances and counterexamples to assertions. Our evaluation focuses on LLMs ability to improve the correctness and completeness of Alloy declarative specifications through automatic repairs. We analyze the results produced by each LLM and compare them with those of leading automatic Alloy repair methods. Our study revealed that while LLMs falls short in comparison to existing techniques in many cases, it was able to successfully repair bugs that no other technique could address. Our analysis also identified errors in LLM generated repairs, including improper operator usage, type errors, higher order logic misuse, relational arity mismatches, hallucination and parsing errors. Additionally, we observed instances of hallucinations in LLM-generated repairs and inconsistency in its results in certain cases. Our study provides valuable insights for software practitioners, researchers, and tool builders considering LLMs for declarative specification repairs.
Instructions:
Readme File contains instructions to navigate in the dataset







