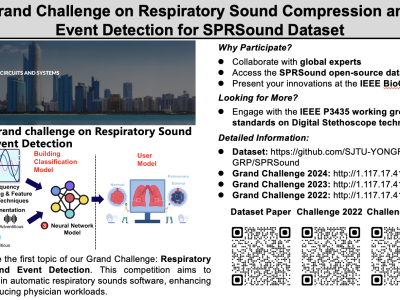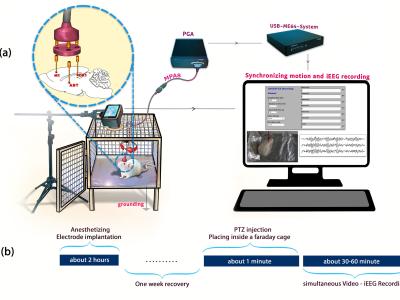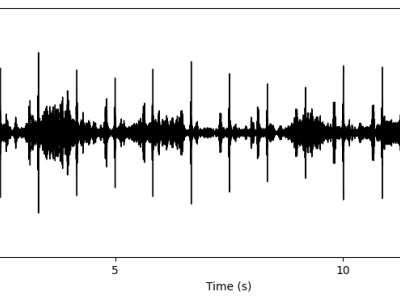
This dataset contains 535 recordings of heart and lung sounds captured using a digital stethoscope from a clinical manikin, including both individual and mixed recordings of heart and lung sounds; 50 heart sounds, 50 lung sounds, and 145 mixed sounds. For each mixed sound, the corresponding source heart sound (145 recordings) and source lung sound (145 recordings) were also recorded. It includes recordings from different anatomical chest locations, with normal and abnormal sounds.
- Categories: