Signal Processing

This dataset is used for machine learning. And the data set is collected in different micro-environments. In this project, ExpoM-RF 4 is used to measure the electric field strength. Four different typs of micro-environments are selected which are urban (6 high population density areas in Kuala Lumpur), suburban (7 low population density areas in Cyberjaya), park (3 park areas) and one indoor micro-environment. From the measurement campaigns, three machine learning (ML) techniques are simulated to model the Electric Field Strength in each micro-environment.
- Categories:
 66 Views
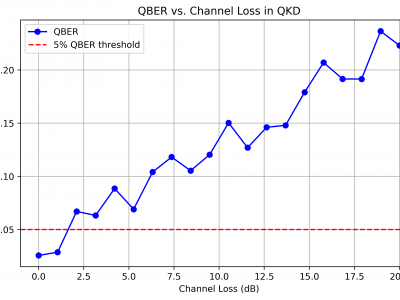
66 ViewsThis dataset supports the research on hybrid quantum encryption by providing simulation results for Quantum Bit Error Rate (QBER) vs. Channel Loss in Quantum Key Distribution (QKD). The dataset includes numerical values used to generate the QBER vs. Channel Loss graph, which illustrates how increasing channel loss impacts quantum encryption performance.
- Categories:
 179 Views
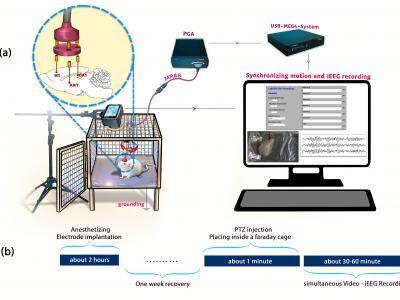
179 ViewsThis database, collected at the Neural Engineering Laboratory, Iran University of Science and Technology, comprises iEEG recordings from Wistar rats during healthy and epileptic conditions. Recordings were collected from 5 rats (3 males, 2 females, weighing 260-378 g and aged 4-5 months). iEEG signals were recorded from 3 brain sites: motor cortex (left M1), thalamus (left ANT), and hippocampus (right CA1) of freely moving rats. As a result, for each rat, a matrix with 3 columns (representing the 3 signals) is available in this dataset.
- Categories:
 564 Views
564 ViewsThis study adopts a comprehensive approach that integrates finite element simulations with experimental validation to investigate the potential application of ultrasonic imaging technology for downhole fallen objects detection. The study first employed finite element simulations to model the impact of fallen objects on acoustic wave propagation, with a focus on examining the correlations between the reflected signal and the fallen objects' spatial position, size, and the probe's excitation frequency.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
A collection of Python pickles objects containing a Pandas DataFrame. Each Dataframe corresponds to the postprocessed firing rate (fr) in Hz and mean amplitude of the spikes (AMP) in microV/s of the vagus nerve recordings obtained from 12 adult female Sprague-Dawley rats. Additionally, the blood-glucose level in mg/dL is included. The fr and AMP signals have 0.1 miliseconds of resolution, whereas the glucose level was measured approximately every 5 minutes. Temporal variations are due to experimental factors. The number of available glucose samples changes across recordings.
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
This dataset is designed for research on 2D Multi-frequency Electrical Impedance Tomography (mfEIT). It includes:
- Categories:
 78 Views
78 ViewsBy collecting the actual measurement data of LRP UWB and HRP UWB array angle measurement devices under the same experimental conditions in a certain underground space, the angle measurement performance of the two devices was compared and analyzed. The results show that the angle measurement performance of the specially designed LRP UWB receiver is superior to that of the HRP UWB receiver.
- Categories:
 166 Views
166 Views
Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) is an emerging technology that utilizes optical fiber (OF) cables as dense arrays of acoustic sensors to detect submarine cable routes. In this study, we combine DAS with ship-board acoustic sources for submarine cable localization. The spatial location of the cable is determined by connecting the coordinates of each DAS channel, which are jointly estimated by the Chan algorithm and a snow ablation optimization algorithm.
- Categories:
 115 Views
115 Views
S D International is a leading dyes & chemicals manufacturer and Supplier with ISO 9001:2015 Certified who offers a vast portfolio of Colorants to our customers across the globe. More than a decade in product development and innovation for the textile industry, our products mainly go into the multiple sectors including the Wood, Paper, Printing Inks, Paints, Coatings, Plastics, Rubber, Food Industry and packaging industries. We supply and export our products in more than 50 countries across the globe.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views