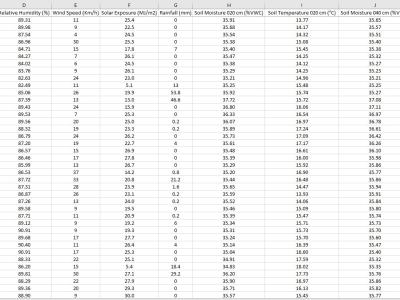
Training and testing the accuracy of machine learning or deep learning based on cybersecurity applications requires gathering and analyzing various sources of data including the Internet of Things (IoT), especially Industrial IoT (IIoT). Minimizing high-dimensional spaces and choosing significant features and assessments from various data sources remain significant challenges in the investigation of those data sources. The research study introduces an innovative IIoT system dataset called UKMNCT_IIoT_FDIA, that gathered network, operating system, and telemetry data.
- Categories: