IoT Based Meat Freshness Classification Using Deep Learning
- Citation Author(s):
-
Zarif Wasif Bhuiyan (Independent University, Bangladesh)Syed Ali Redwanul Haider (Independent University, Bangladesh)Adiba Haque (Independent University, Bangladesh)Mohammad Rejwan Uddin (Independent University, Bangladesh)Mahady Hasan (Independent University, Bangladesh)
- Submitted by:
- Zarif Wasif Bhuiyan
- Last updated:
- DOI:
- 10.21227/tz42-s971
- Data Format:
 657 views
657 views
- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
This paper presents an innovative Internet of Things (IoT) system that integrates gas sensors and a custom Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to classify the freshness and species of beef and mutton in real time. The CNN, trained on 9,928 images, achieved 99% accuracy, outperforming models like ResNet-50, SVM, and KNN. The system uses three gas sensors (MQ135, MQ4, MQ136) to detect gases such as ammonia, methane, and hydrogen sulfide, which indicate meat spoilage. Real-time feedback is provided via LED indicators (green for fresh, yellow for partially fresh, red for rotten), with results displayed on an LED screen. This IoT system offers an efficient and reliable solution for real-time meat quality monitoring.
Instructions:
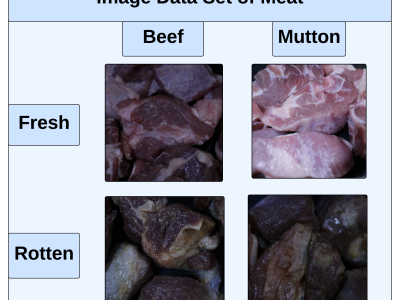
This research integrates deep learning models, gas sensor data, and IoT technology to classify meat species and assess meat freshness in real-time, creating a comprehensive solution for ensuring meat quality and safety. High-resolution images of fresh and rotten meat were captured at two key time points, with fresh meat photographed at 0 hours and rotten meat after 48 hours of spoilage. The dataset includes 6,672 images for meat freshness classification and 3,256 images for species classification. To improve model generalization and performance, data augmentation techniques such as rotation, scaling, flipping, and color adjustments were applied, resulting in a larger and more diverse dataset.








great