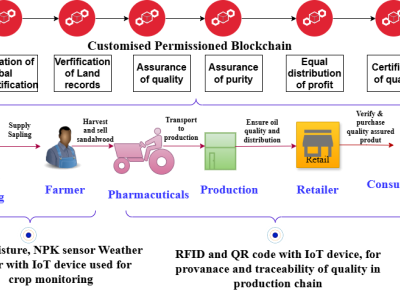
Securing smart grids relies in part on the reliable integration of blockchain technologies for the automation of energy transactions. However, the presence of vulnerabilities in smart contracts poses a direct threat to the integrity and resilience of these critical systems. This work presents a unique and structured dataset of real-world vulnerabilities observed in smart contracts, intended for cybersecurity research applied to smart energy infrastructures.
- Categories: