Artificial Intelligence
This paper explores public perceptions surrounding the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in cultural and media production across the Arab region. Based on a comprehensive questionnaire distributed among 2000 participants, the study investigates attitudes toward AI-driven content, ethical concerns, cultural identity threats, educational impacts, and legal responsibilities.
- Categories:
 96 Views
96 ViewsDigital microfluidics are a unique technique for operation of nano-to-micro liter droplets based on electrowetting on dielectric. It has great application potential in the field on clinic diagnosis, life science and environment monitoring. Due to the fast droplet moving speed and high degree of freedom for droplet manipulation, it is urgent to develop automated and intelligent approaches for droplet monitoring and control.
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views
Semantic code search, retrieving code that matches a given natural language query, is an important task to improve productivity in software engineering. Existing code search datasets face limitations: they rely on human annotators who assess code primarily through semantic understanding rather than functional verification, leading to potential inaccuracies and scalability issues. Additionally, current evaluation metrics often overlook the multi-choice nature of code search. This paper introduces CoSQA+, pairing high-quality queries from CoSQA with multiple suitable codes.
- Categories:
 4 Views
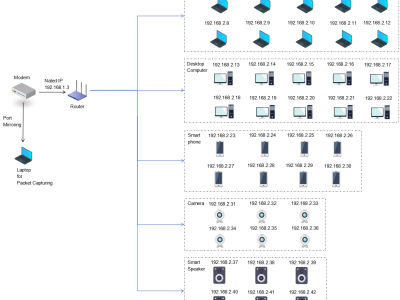
4 Viewsthree-level network topology experimental environment was constructed based on a typical home network. An optical network terminal (Bell XE-140W-TD) was used as the starting point for Internet access, and a Gigabit wired connection was established with the core router (Huawei TC30) via a shielded Cat 6 cable. This router is a Huawei beta version that can obtain specific device information and corresponding traffic after NAT. The experimental evaluation of traffic attribution association in subsequent chapters will use this as ground truth label data for comparison.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
This dataset provides packet traces captured in a realistic 5G Vehicle-to-Everything (5G-V2X) environment, encompassing both legitimate vehicular communications and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. By deploying four user equipments (UEs) under multiple attacker configurations, the collected captures reflect various DDoS types (TCP SYN, UDP, and mixed) and reveal their impact on 5G-V2X networks. The dataset is further enriched with Argus files and CSV feature tables, facilitating data-driven approaches such as Machine Learning (ML)-based detection agents.
- Categories:
 375 Views
375 Views
This is the dataset for paper VI-BEVSEG training and testing. For more details about the dataset structure, please refer to Nuscense or V2X-Sim. We only use the number 1 vehicle in the V2X-Sim dataset. Replace the folder in this dataset, and only keep the vehicle 1 six onboard cameras information, infrastructure camera information and their semantic camera information in 'sweeps' and 'samples' folder. Then replace the 'v1.0-trainval' folder with ours and put the h5 maps under V2X-Sim folder.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
This is the dataset for paper VI-BEVSEG training and testing. This dataset mostly inherits from V2X-Sim dataset. Follow the same dataset structure as the V2X-Sim dataset. Follow the V2X-Sim instruction to use. The only change we made is adding some 'h5' ground truth semantic maps. And we only keep the vehicle 1 camera information and infrastructure camera information.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views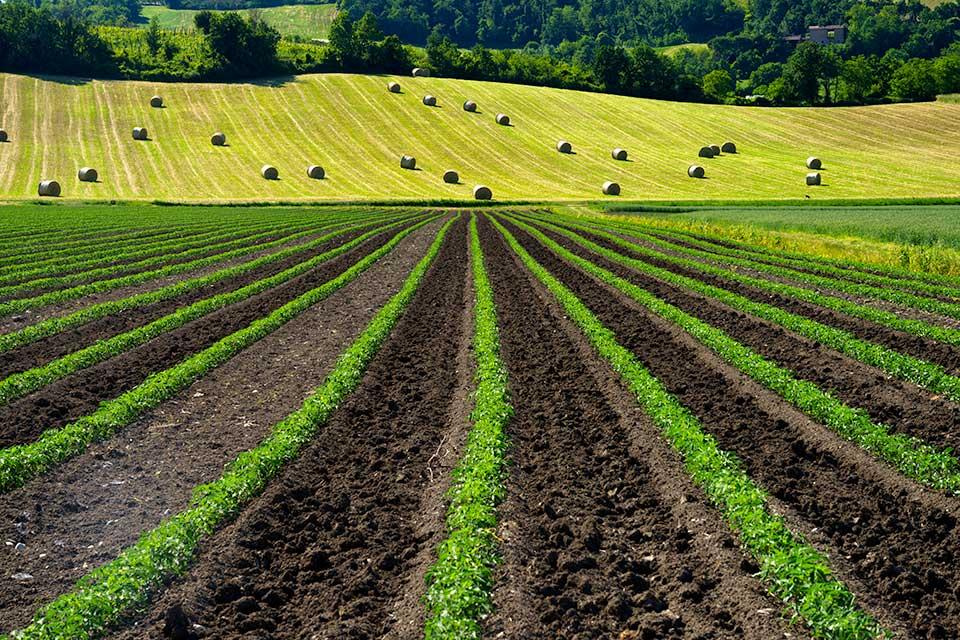
This dataset presents longitudinal measurements of plant growth characteristics under varying lighting conditions. Collected for 30 individual plants, the data spans multiple time points and includes key variables such as plant fresh weight (g), plant height (mm), plant width (mm), and number of leaves. Each measurement is associated with a specific plant, date (DD/MM/YYYY), experimental group, and a lighting recipe defined by the percentage composition of Red, Green, and Blue light.
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views
When artificial intelligence (AI) systems take actions or make decisions, the issue of accountability for the outcomes or decisions made by AI systems comes into question. The rapid advancement of AI technology poses a greater challenge, as current legal and ethical frameworks struggle to keep up with innovation, resulting in a lack of standardization in existing policies that comprehensively address accountability in AI.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views