*.csv
The proliferation of IoT devices which can be more easily compromised than desktop computers has led to an increase in the occurrence of IoT-based botnet attacks. In order to mitigate this new threat there is a need to develop new methods for detecting attacks launched from compromised IoT devices and differentiate between hour and millisecond long IoT-based attacks.
- Categories:
 21 Views
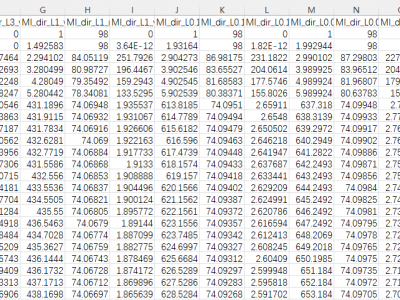
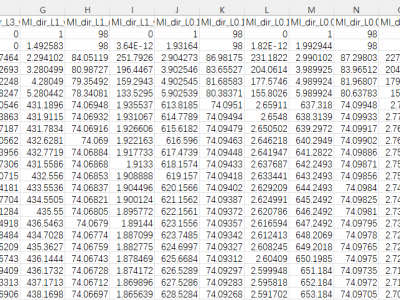
21 ViewsMany Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) has been proposed in the current decade. To evaluate the effectiveness of the IDS Canadian Institute of Cybersecurity presented a state of art dataset named CICIDS2017, consisting of latest threats and features. The dataset draws attention of many researchers as it represents threats which were not addressed by the older datasets. While undertaking an experimental research on CICIDS2017, it has been found that the dataset has few major shortcomings. These issues are sufficient enough to biased the detection engine of any typical IDS.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
<p><span style="font-family: 'Times New Roman'; font-size: medium;">This is the data set used for The Third International Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining Tools Competition, which was held in conjunction with KDD-99 The Fifth International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. The competition task was to build a network intrusion detector, a predictive model capable of distinguishing between ``bad'' connections, called intrusions or attacks, and ``good'' normal connections.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
We collect metadata including published year and keywords for 84,725 papers published in 42 statistical journals from 1992 to 2021 from the Web of Science (www.webofscience.com). After combining different expressions of the same keyword and filtering out keywords with low frequency, we finally obtain 5,037 keywords. Multiple keywords co-exist within a paper, and this co-occurrence relationship can be utilized to construct the keyword co-occurrence network.
- Categories:
 24 Views
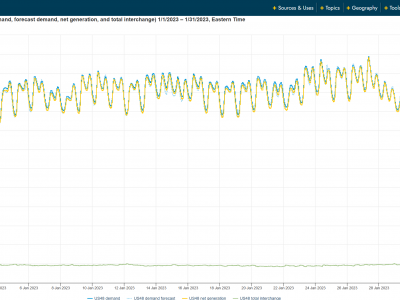
24 ViewsThis dataset contains hourly electricity demand data and corresponding weather indicators collected from 2021 to 2023. The electricity data was sourced from the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), covering both winter and summer periods across three years. Weather features—including temperature, wind speed, and humidity—were collected to capture the external conditions affecting demand. All files are stored in CSV format and aligned by timestamp. This dataset supports research in time series forecasting, demand prediction, and energy systems modeling.
- Categories:
 123 Views
123 Views
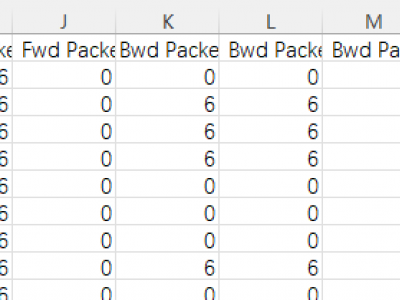
Droidware is an Android malware dataset developed at the Cybersecurity Lab, GLA University, India. It comprises 253,527 applications, including 129,950 benign and 123,577 malicious samples. The dataset captures 68 features extracted from function call graphs, permissions, and Java source code, providing a comprehensive view of Android malware behavior. This latest and up-to-date dataset supports the training of AI-based malware detection models, aiding in the development of robust malware classification and threat mitigation strategies for cybersecurity research.
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 ViewsThis dataset comprises volatile organic compound (VOC) profiles collected from blood culture broth samples using an electronic nose (E-nose) system. The samples include cultures positive for Candida spp., including C. albicans, C. glabrata, C. tropicalis, among others, as well as negative control samples.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
A rapid growth of wireless communication networks, particularly in 5G Non-Standalone (NSA) deployments, has necessitated advanced multiple access techniques to enhance spectral efficiency, interference management, and energy optimization [1-3]. Rate-Splitting Multiple Access (RSMA) has arisen as a strong candidate to replace conventional Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) by efficiently splitting user data into common and private components. [1-2].
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views