Datasets
Standard Dataset
Wearable Respiratory Data During Pulmonary Rehabilitation Exercises (Magnetic Field-Based and Piezoelectric-Based Wearables Against Airflow Transducer)
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Ana Carmo
- Last updated:
- Thu, 05/16/2024 - 10:13
- DOI:
- 10.21227/tkxr-xf96
- Data Format:
- Links:
- License:
 146 Views
146 Views- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
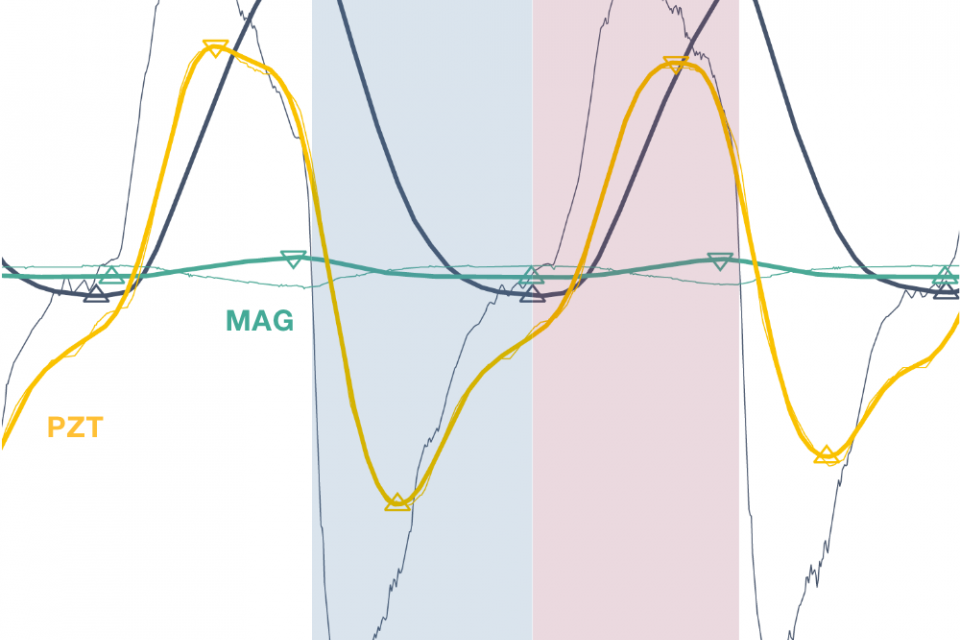
Dataset for validation of a new magnetic field-based wearable breathing sensor (MAG), which uses the movement of the chest wall as a surrogate measure of respiratory activity. Based on the principle of variation in magnetic field strength with the distance from the source, this system explores Hall effect sensing, paired with a permanent magnet, embedded in a chest strap.
The proposed wearable device was evaluated using the gold-standard as a reference system - an airflow transducer - and compared to a commonly used wearable device with analogous usability but with a different working principle - a piezoelectric-based sensor (PZT) embedded in a chest strap.
A total of 16 healthy participants (M/F parity) performed 15 different activities, representative of pulmonary rehabilitation exercises, simultaneously using the three devices. The dataset was created for evaluation of the proposed device based on detection of flow reversal events, as well as fiducials detection latency.
The 15 activities executed by the participants were: standing normal breathing (STNB); seated normal breathing (SNB); seated guided-breathing (SGB); normal/deep-alternated breathing (MIXB); march (MCH); squat (SQT); adduction/abduction of the left/right arm (AAL/AAR); adduction/abduction of the left/right leg (ALL/ALR); upwards (overhead) left/right arm extension (UAL/UAR); shoulder elevation (SE); side stretch (SS); and seated trunk rotation (TR).
The dataset consists of 239 CSV acquisition files, corresponding to each of the 16 participants performing each of the 15 activities (except one participant that did not perform one of the activities).
Each file, corresponding to an activity performed by one of the participants, contains a dictionary with information regarding the acquisition (first line of the file, identified with a # symbol) and a dataframe (tab separated) containing the data from the three devices in raw (before processing) and preprocessed for flow reversal extraction (as explained below).
Processing:
Considering that the working principles of the three sensors are distinct, the respiration signals obtained from the three devices are subject to different interpretations. For example, an inspiration event produces an upward shift in the signals from the piezoelectric-based sensor (PZT) and airflow transducer, but a downward shift in the case of the magnetic field-based sensor (MAG). Moreover, in the case of both wearables, the start and ending of the inspiration phase align with valleys and peaks in the signals [1], whereas in the signal from the airflow transducer these events correspond to zero-crossings [2].
In order to even out the interpretation of the different signals, the respiratory data obtained from our sensor were inverted and the data from the airflow transducer were subjected to numerical integration, following a procedure similar to the calibration method described in [3]. As such, the valleys and peaks became events of flow reversal, precisely indicating the beginning of the inspiration and expiration phases of respiration.
Accessing data from a file (Python example):
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv(filepath, sep='\\t', comment='#')
Files are named as [participant ID]_[activity ID].csv
Additional information is provided in the following JSON files:
-
participant_metadata.json: dictionary containing participant demographics and anthropometric characteristics, in the format:
{
“D4GQ”: {”Age range”: “40-49”, “Sex”: “M”, “Thoracic circumference (mm)”: 96.8, “Chest strap circumference”: 89.0},
…
}
-
activities.json: dictionary containing the activities acronyms as keys and the full activity designations as values.
References:
[1] A. Allataifeh and M. Al Ahmad, “Simultaneous Piezoelectric Noninvasive Detection of Multiple Vital Signs,” Scientific Reports, vol. 10, no. 1, p. 416, Jan. 2020
[2] M.-A. Oestreich et al., “Breath Detection Algorithms Affect Multiple-Breath Washout Outcomes in Pre-School and School Age Children,” PLoS ONE, vol. 17, no. 10, p. e0275866, Oct. 2022.
[3] C. Nguyen et al., “An Automated and Reliable Method for Breath Detection During Variable Mask Pressures in Awake and Sleeping Humans,” PLoS One, vol. 12, no. 6, Jun. 2017.