Temperature control
The problem of cooling in rescue robots is similar to that of the entire domain of product development involving electronic systems. When considering mission-oriented rescue robots, this issue becomes more severe, as the tolerance to failure is remarkably low. While cooling is considered indispensable, the hazardous environmental condition of the scene of deployment, comprising of water, dust, toxic gases, or fire, constrains the choices of the method.
- Categories:
 301 Views
301 ViewsMore than 40% of energy resources are consumed in the residential buildings, and most of the energy is used for heating. Improving the energy efficiency of residential buildings is an urgent problem. The collected data is intended to study a dependence of the dynamics heat energy supply from outside temperature and houses characteristics, such as walls material, year of construction, floors amount, etc. This study will support the development of methods for comparing thermal characteristics of residential buildings and carry out recommendations for the energy efficiency increases.
- Categories:
 458 Views
458 ViewsMore than 40% of energy resources are consumed in the residential buildings, and most of the energy is used for heating. Improving the energy efficiency of residential buildings is an urgent problem. The collected data is intended to study a dependence of the dynamics heat energy supply from outside temperature and houses characteristics, such as walls material, year of construction, floors amount, etc. This study will support the development of methods for comparing thermal characteristics of residential buildings and carry out recommendations for the energy efficiency increases.
- Categories:
 1059 Views
1059 Views
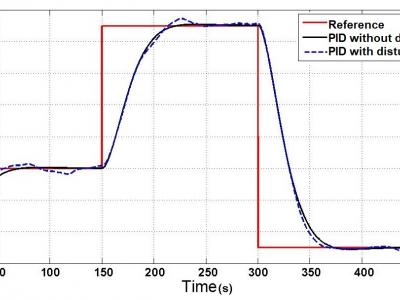
In this paper, a PID controller is applied in order to control the temperature by a proposed model of Newton’s law of cooling. The control problem considers a model obtained, which the temperature of a body decreases with time is proportional to the difference in temperature between the body and its surroundings.
- Categories:
 198 Views
198 ViewsIn this paper, a PID controller is applied to control the temperature to a proposed model derived of the Newton’s law of cooling. The control problem considers a second-order model obtained that the rate at which the temperature of a body decreases with time is proportional to the difference in temperature between the body and its surroundings. This model represents a mathematical function the device's output for each possible input with initial conditions zero.
- Categories:
 741 Views
741 Views