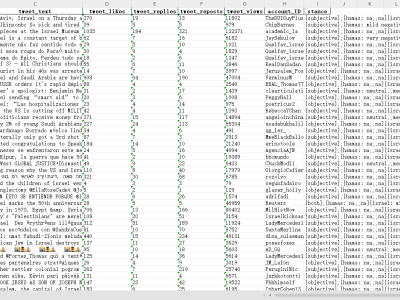
This dataset provides the foundational resources for evaluating and optimizing Formula L , a novel mathematical framework for semantic-driven task allocation in multi-agent systems (MAS) powered by large language models (LLM). The dataset includes Python code and both empirical and synthetic data, specifically designed to validate the effectiveness of Formula L in improving task distribution, contextual relevance, and dynamic adaptation within MAS.
The dataset comprises:
- Categories: