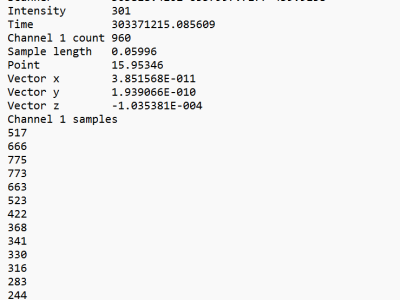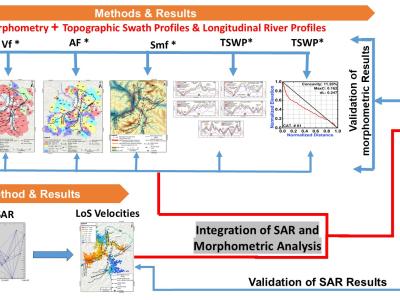
Abstract—This study evaluates the long-term tectonic influence on landform development as well as the present-day tectonic activity in the Nanga Parbat-Haramosh Syntaxis (NPHS), a geologically complex region in the northwestern Himalayas. Using geomorphic indices and remote sensing techniques, including Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) and existing Global Positioning System (GPS) data, this research identifies significant neotectonic deformation, with active faults contributing to slope hazards and seismic risks.
- Categories: