Machine Learning
A monitoring data, which includes several OTDR traces incorporating various types of fiber events (e.g. reflective, non-reflective, merged events) induced along an optical fiber link, is provided. Different fiber faults such as fiber cut, and fiber bend are modeled using optical components such as connectors and variable optical attenuators (VOAs). The data can be used to train machine learning models for solving fiber fault diagnosis problems.
- Categories:
 1010 Views
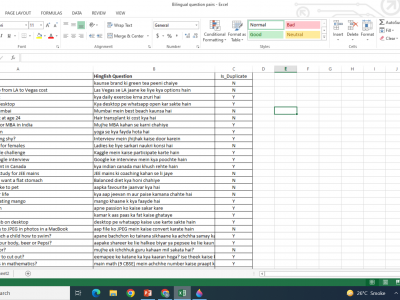
1010 ViewsAlthough asking and replying on social media platforms in mixed language is a very common phenomenon these days, there is lack of precise corpora to analyze such code mixed language. Datasets released by various CQA sites are monolingual i.e. only in English language. To perform our task, we needed annotated bilingual dataset which include Question pairs in mashed up language. In view of this scarcity we created a dataset by scraping pairs of questions from distinct social media networks, for-example Yahoo!
- Categories:
 122 Views
122 Views
The dataset contains labeled sentences. The sentences having information related to (1) infections, (2) suffering from pneumonea, (3) deaths, and (4) health updates from government/WHO, are labeled with 1 and the rest are labeled with 0. Source of all the news articles: https://www.thehindu.com/archive/
- Categories:
 128 Views
128 ViewsThe monitored data is obtained using the optical time domain reflectometry (OTDR) principle, which is commonly used for troubleshooting fiber optic cables or links. The data set contains raw OTDR traces that include one or two reflective events caused by the placement of one or two reflectors and/or an open physical contact (PC) at the end of the monitored optical fiber link.
- Categories:
 1752 Views
1752 ViewsPROTEIN STRUCTURE AND SYNTHETIC MULTI-VIEW CLUSTERING DATASETS
Multi-View Clustering (MVC) datasets used in the following paper:
Evolutionary Multi-objective Clustering Over Multiple Conflicting Data Views. Authors: Mario Garza-Fabre, Julia Handl, and Adán José-García. IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON EVOLUTIONARY COMPUTATION. Accepted for publication, November 2022.
This entry contains all 420 datasets used in the paper, including:
- Categories:
 249 Views
249 ViewsThis synthetic dataset is generated using Matlab automotive driving toolbox to simulate a 77GHz FMCW millimeter-wave radar sensing in the road scenario. Especially for the Doppler ambiguity case, when the object vehicles move within or out of the unambiguous detecable velocity range. The dataset contains in total 20 recordings with the duration of 1 second each. Both time-division modulation (TDM) and binary phase modulation (BPM) data are provided. Each recording consists of complex ADC raw data and complex range-Doppler map, together with the ground-truth range and velocity.
- Categories:
 409 Views
409 Views
Biometric management and that to which uses face, is indeed a very challenging work and requires a dedicated dataset which imbibes in it variations in pose, emotion and even occlusions. The Current work aims at delivering a dataset for training and testing purposes.SJB Face dataset is one such Indian face image dataset, which can be used to recognize faces. SJB Face dataset contains face images which were collected from digital camera. The face dataset collected has certain conditions such as different pose, Expressions, face partially occluded and with a uniform attire.
- Categories:
 2708 Views
2708 ViewsEvolving from the well-known ray-tracing dataset DeepMIMO, the DeepVerse 6G dataset additionally provides multi-modal sensing data generated from various emulators. These emulators provide the wireless, radar, LiDAR, vision and position data. With a parametric generator, the DeepVerse dataset can be customized by the user for various communication and sensing applications.
- Categories:
 109 Views
109 ViewsBeam management is a challenging task for millimeter wave (mmWave) and sub-terahertz communication systems, especially in scenarios with highly-mobile users. Leveraging external sensing modalities such as vision, LiDAR, radar, position, or a combination of them, to address this beam management challenge has recently attracted increasing interest from both academia and industry. This is mainly motivated by the dependency of the beam direction decision on the user location and the geometry of the surrounding environment---information that can be acquired from the sensory data.
- Categories:
 974 Views
974 Views