Unpaired MR-CT Brain Dataset for Unsupervised Image Translation
- Citation Author(s):
-
Waleed Mahafza (Jordan University Hospital)
- Submitted by:
- Omar Al-Kadi
- Last updated:
- DOI:
- 10.21227/fe9x-qg64
- Links:
 2686 views
2686 views
- Categories:
Abstract
The Magnetic Resonance – Computed Tomography (MR-CT) Jordan University Hospital (JUH) dataset has been collected after receiving Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval of the hospital and consent forms have been obtained from all patients. All procedures followed are consistent with the ethics of handling patients’ data.
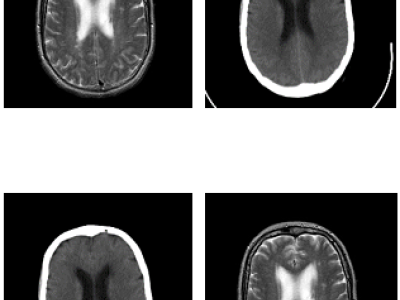
The dataset consists of unpaired brain CT and MR images of 20 patients scanned for radiotherapy treatment planning for brain tumors. The dataset contains T2-MR and CT images for patients aged between 26-71 years with mean-std equal to 47-14.07. The MR images were acquired with a 5.00mm T Siemens Verio 3T using a T2-weighted without contrast agent, 3 Fat sat pulses (FS), 2500-4000 TR, 20-30 TE, and 90/180 flip angle. The CT images were acquired with Siemens Somatom scanner with 2.46mGY.cm dose length, 130KV voltage, 113-327 mAs tube current, topogram acquisition protocol, 64 dual source, one projection, and slice thickness of 7.0mm. Smooth and sharp filters have been applied to CT images. The MR scans have a resolution of 0.7×0.6×5 mm^3, while the CT scans have a resolution of 0.6×0.6×7 mm^3.
Instructions:
There are a total of 179 2D axial image slices referring to 20 patient volumes (90 MR and 89 CT 2D axial image slices). The dataset contains MR and CT brain tumour images with corresponding segmentation masks.







In reply to please provide me data base by Satyanarayana P
I am writing to request access to the unpaired MRI-CT dataset you are offering. I am currently working on a research project that focuses on the translation of CT scans to MRI using deep learning techniques, particularly generative models such as CycleGAN and its variants.
The aim of this project is to explore the potential of synthetic MRI generation from CT images, which could help reduce patient exposure to radiation while maintaining diagnostic quality. The unpaired nature of your dataset is particularly well-suited to my study, as it reflects the kind of data scarcity and distribution mismatch often encountered in clinical practice.
This dataset will play a key role in an upcoming publication I am preparing, where I intend to benchmark different architectures for CT-to-MRI synthesis and evaluate their performance across anatomical and modality-specific metrics.
I assure you that the dataset will be used strictly for academic and non-commercial research purposes. I would be grateful for your consideration, and I am happy to comply with any usage terms or attribution requirements you may have.
Thank you for your time and support.
In reply to Dear sir,I am a student,I by yang yao
In reply to Please grant me to access the by Cheng-Lin Tsai