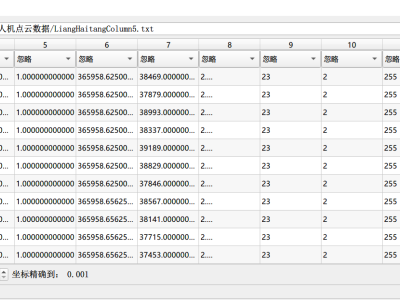
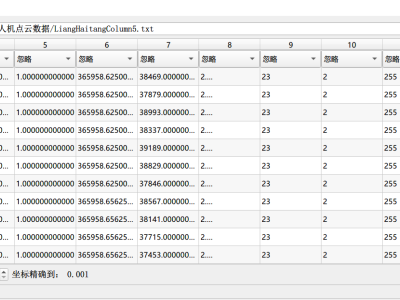
The Baseline set described in the IEEE article (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10077565) as Baseline_set contains 1442450 rows, where the number of rows varied between 15395 and 197542 for the 16 subjects; the average per subject being 69095 rows. The data set is filtered and standardized as described in III.C in the submission . The other data sets used in the article are derived from Baseline set.
- Categories: