Artificial Intelligence

All the healthcare facilites in this dataset were collected from the MOH 2018 list of Uganda healthcare facilites (https://library.health.go.ug/sites/default/files/resources/National%20Health%20Facility%20MasterLlist%202017.pdf) Additional features were scraped using the Google Maps API and additionally from some of the websites of the healthcare facilities themselves.
- Categories:
 69 Views
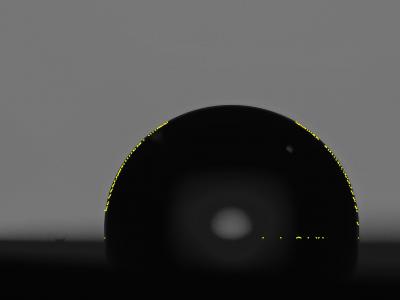
69 ViewsThis paper describes a dataset of droplet images captured using the sessile drop technique, intended for applications in wettability analysis, surface characterization, and machine learning model training. The dataset comprises both original and synthetically augmented images to enhance its diversity and robustness for training machine learning models. The original, non-augmented portion of the dataset consists of 420 images of sessile droplets. To increase the dataset size and variability, an augmentation process was applied, generating 1008 additional images.
- Categories:
 161 Views
161 Views
The datasets used for TASLP manuscript. These datasets are widely recognized and validated within the summarization research community, and using these well-established datasets ensures that our results are comparable with the vast majority of related work.In each dataset, we use 80% as the training set, while the remaining 20% as the test data. The range of datasets used for collecting knowledge is also consistent with the above. For the large dataset, we only use a part of it because collecting knowledge is time-consuming.
- Categories:
 30 Views
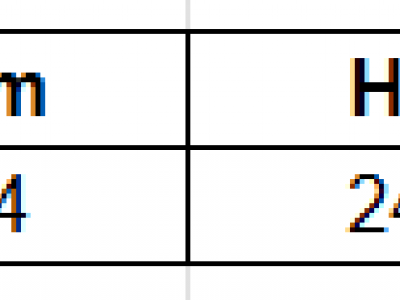
30 ViewsThe Hindi Spam SMS Dataset comprises 3,894 messages, each labeled as either spam or ham. This dataset was meticulously curated with contributions from students who encountered these messages daily. The messages were collected from their experiences and those shared by friends and peers, ensuring a diverse and realistic representation of SMS communication in Hindi. It offers a representative sample of real-world Hindi text messages for analysis. The dataset primarily contains messages written in Hindi, reflecting its origin's linguistic and cultural context.
- Categories:
 110 Views
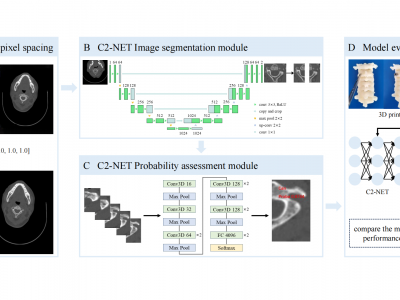
110 ViewsThe lack of an objective and ready-to-use tool for preoperative planning in C2 pedicle screw placement surgery is notable. We developed C2-Net, a deep learning model for rapidly and accurately assessing C2 pedicle screw placement feasibility from CT images. C2-Net incorporates image segmentation and screw placement probability assessment modules.
- Categories:
 77 Views
77 ViewsDig21000 is a comprehensive dataset consisting of 21,000 images of digit-based rotary meters photographed in uncontrolled environments.
It integrates images from open datasets on the Roboflow platform and those independently collected.
After undergoing cleaning, the images are randomly divided into training and testing sets at a ratio of 6:1.
It contains 10 digit categories. The images are affected by multiple factors and can be used for research on digital dial recognition. It is publicly available and citation is required when using it.
- Categories:
 92 Views
92 ViewsTo further evaluate the practical performance of HPDM, we apply it to detect defects in actual industrial circuit boards. Various defects, such as board, lifting, and ffipping defects, occur on the circuit board because of external forces imposed during the placement and soldering processes .A real industrial circuit board defect detection dataset is collected and presented. This dataset includes five different categories of components with various real multiscale defects.
- Categories:
 171 Views
171 Views
To ensure reproducible experiments and prevent overburdening the server, we construct an SQL-based database dubbed RiPAMI (Reviews in Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, pronounced as \textipa{/ri:p\ae mi/}). This database stores information related to the paper such as title, abstract, date of publication, venue, citation counts, and reference details, etc. From initial keyword selection to the final SQL-based RiPAMI snapshot, three key steps are implemented to ensure the data in RiPAMI is clean, accurate, and reliable.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
Large vision-language models (LVLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in multimodal understanding and generation tasks. However, these models occasionally generate hallucinatory texts, resulting in descriptions that seem reasonable but do not correspond to the image. This phenomenon can lead to wrong driving decisions of the autonomous driving system.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views