Power and Energy
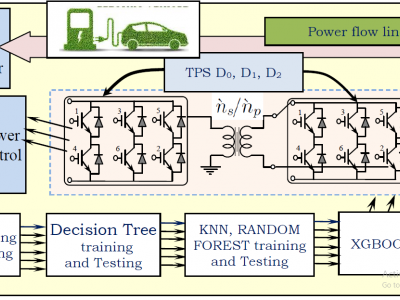
Dual active bridge (DAB) converter is an important converter for electric vehicles, energy storage systems. Data sets are introduced to control the DC-DC power control. Triple phase-shift of DAB is controlled by the range of zero voltage switching. Optimal switching to reduce high current stress DC-DC converter is In presented data sets are used with python program to execute the different stages of machine learning. Performance of all stages are well addressed each data output file.
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 ViewsDual active bridge (DAB) converter is an important converter for electric vehicles, energy storage systems. Data sets are introduced to control the DC-DC power control. Triple phase-shift of DAB is controlled by the range of zero voltage switching. Optimal switching to reduce high current stress DC-DC converter is In presented data sets are used with python program to execute the different stages of machine learning. Performance of all stages are well addressed each data output file.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
High-power radio frequency converters (RFCs) need to deliver a wide-range power against variable load impedance. However, it is difficult to achieve a wide-range power regulation and zero voltage switching (ZVS) simultaneously. To address thi.s issue, this paper proposes a DC-link parallel AC-link series (DPAS) multiple power amplifier (MPA) architecture with outphasing modulation. The generalized mathematical model of the proposed topology is presented. The system’s soft-switching range and criterion are analyzed.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
An In-depth Analysis of Thermal Management Systems for Wireless Charging in Electric Vehicles
1. Introduction
Wireless charging technology is revolutionizing electric vehicles (EVs) by offering a convenient alternative to traditional charging. This technology enhances user experience and supports the growth of autonomous EV fleets. As electrification of transportation accelerates, effective thermal management becomes crucial to address heat generation during inductive power transfer, ensuring system reliability and longevity.
- Categories:
 114 Views
114 ViewsThis dataset provides a comprehensive record of wind power generation and its relationship with oceanic-atmospheric indices, facilitating advanced forecasting and analytical research in renewable energy. The dataset comprises 12 input parameters, including average wind speed, which serves as a crucial predictor, while wind power generation acts as the output variable.
- Categories:
 160 Views
160 ViewsThe recent developments in the field of the Internet of Things (IoT) bring alongside them quite a few advantages. Examples include real-time condition monitoring, remote control and operation and sometimes even remote fault remediation. Still, despite bringing invaluable benefits, IoT-enriched entities inherently suffer from security and privacy issues. This is partially due to the utilization of insecure communication protocols such as the Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) 1.6. OCPP 1.6 is an application-layer communication protocol used for managing electric vehicle chargers.
- Categories:
 700 Views
700 Views
Self-Aligning IPT Pads for Efficient High-Power Wireless Charging for EV
Introduction
- Categories:
 76 Views
76 Views
The aim of this paper is to propose a method of control of a universal input power source station for the production of electricity composed of conventional sources and renewable energy sources as well as a storage element.The development and the design of a three-phase grid connected inverter was studied. The research was able to reach its objectives by designing, modelling, analysis and simulations of the circuit using Psim software package that have helped to check the performance of the proposed control system.
- Categories:
 84 Views
84 Views
This paper provides a comprehensive evaluation of the BESS's optimum size targets, limitations, methodology, benefits and disadvantages. Furthermore, energy storage technologies and improved application targets have been presented and discussed for greater clarity. This study focuses primarily on BESS deployments, methodologies, and environmental impact. BEES innovations and achievements for electrical networks are also compared to other energy storage technologies. Concerns and obstacles are discussed to offer researchers in BESS a comprehensive picture.
- Categories:
 123 Views
123 Views
The current paper examines and highlights the numerous energy storage system (ESS) technologies used in microgrids, as well as their architectures, configurations, performances, benefits, and drawbacks, also by providing a tangible outline for prospective efficient and sustainable ESS. As a result, there is also a comparison of the various technologies. As a consequence, there is also a comparison of the different technologies. Finally, some of the present ESS concerns and difficulties are explored.
- Categories:
 83 Views
83 Views