Evidence Detection in Cloud Forensics

- Citation Author(s):
-
Prasad Purnaye (Researcher, MIT World Peace University, India)Vrushali Kulkarni (Professor, MIT World Peace University, India)
- Submitted by:
- Prasad Purnaye
- Last updated:
- DOI:
- 10.21227/2yr5-7z67
- Data Format:
- Links:
 3106 views
3106 views
- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
Cloud forensics is different than digital forensics because of the architectural implementation of the cloud. In an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) cloud model. Virtual Machines (VM) deployed over the cloud can be used by adversaries to carry out a cyber-attack using the cloud as an environment. Investigation of such a crime requires sufficient evidence data to prove the attack in the court of law. Electronic evidence (EE) is any data that produce information relevant to the investigation. Identifying evidence from the data generated in a cloud environment is a tedious and manual process. Adhering to RFC 3227 the evidence collection can be carried out once the evidence data is detected with appropriate triage.
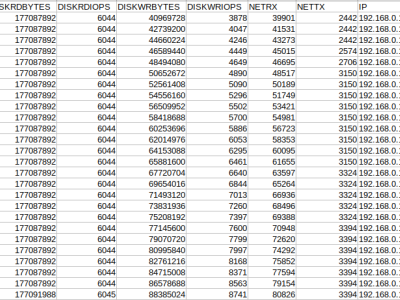
Cyber attack originating from a VM leaves its trails on the resource that it utilizes. These patterns of attacks on the resource and its properties can be used to detect and acquire evidence data generated in a cloud.
We have generated a dataset using the following settings:
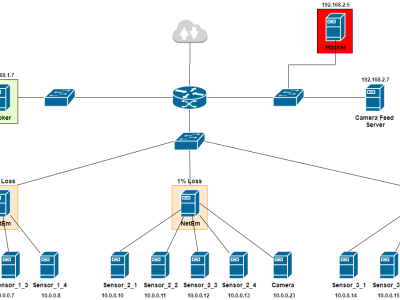
To generate the dataset a private cloud was set up. The system configuration included Intel® CoreTM i5-4590 Processor with 12 GB of RAM with 1TB of HDD. The private cloud setup was done using a KVM type-1 hypervisor along with OpenNebula (version 5.12) as a cloud management platform. To simulate the real-time cloud environment a script generating synthetic workload was deployed on the virtual machines of the cloud. An attack was carried out. The dataset is manually tagged with the known state of attack or normal to respective VM.
Instructions:
About the dataset
The dataset generated is a KVM monitoring dataset however we proposed a novel feature-set. The methodology used to generate these novel features is explained in https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/comp-2022-0241/html.
where the features can be used to train ML models for evidence detection.
The second portion of the dataset is published under the standard dataset of IEEE Dataport under the name of Memory Dumps of Virtual Machines for Cloud Forensics.
How to use
These two datasets can be used together as they are the outcome of the same experiment. Memory dumps have timestamp and VMID, UUID features.
or
This Dataset can be used to study the impact of an attack (origin) on the Rate of Resource utilization of a VM monitored at the hypervisor.
Sr No | Category | Feature | Description |
1 | Meta-data | LAST_POLL | epoch timestamp |
2 | VMID | The ID of the VM | |
3 | UUID | unique identifier of the domain | |
4 | dom | domain name | |
5 | Network | rxbytes_slope | Rate of received bytes from the network |
6 | rxpackets_slope | Rate of received packets from the network | |
7 | rxerrors_slope | Rate of the number of receive errors from the network | |
8 | rxdrops_slope | Rate of the number of received packets dropped from the network | |
9 | txbytes_slope | Rate of transmitted bytes from the network | |
10 | txpackets_slope | Rate of transmitted packets from the network | |
11 | txerrors_slope | Rate of the number of transmission errors from the network | |
12 | txdrops_slope | Rate of the number of transmitted packets dropped from the network | |
13 | Memory | timecpu_slope | Rate of time spent by vCPU threads executing guest code |
14 | timesys_slope | Rate of time spent in kernel space | |
15 | timeusr_slope | Rate of time spent in userspace | |
16 | state_slope | Rate of running state | |
17 | memmax_slope | Rate of maximum memory in kilobytes | |
18 | mem_slope | Rate of memory used in kilobytes | |
19 | cpus_slope | Rate of the number of virtual CPUs chaged | |
20 | cputime_slope | Rate of CPU time used in nanoseconds | |
21 | memactual_slope | Rate of Current balloon value (in KiB) | |
22 | memswap_in_slope | Rate of The amount of data read from swap space (in KiB) | |
23 | memswap_out_slope | Rate of The amount of memory written out to swap space (in KiB) | |
24 | memmajor_fault_slope | Rate of The number of page faults where disk IO was required | |
25 | memminor_fault_slope | Rate of The number of other page faults | |
26 | memunused_slope | Rate of The amount of memory left unused by the system (in KiB) | |
27 | memavailable_slope | Rate of The amount of usable memory as seen by the domain (in KiB) | |
28 | memusable_slope | Rate of The amount of memory that can be reclaimed by balloon without causing host swapping (in KiB) | |
29 | memlast_update_slope | Rate of The timestamp of the last update of statistics (in seconds) | |
30 | memdisk_cache_slope | Rate of The amount of memory that can be reclaimed without additional I/O, typically disk caches (in KiB) | |
31 | memhugetlb_pgalloc_slope | Rate of The number of successful huge page allocations initiated from within the domain | |
32 | memhugetlb_pgfail_slope | Rate of The number of failed huge page allocations initiated from within the domain | |
33 | memrss_slope | Rate of Resident Set Size of the running domain's process (in KiB) | |
34 | Disk | vdard_req_slope | Rate of the number of reading requests on the vda block device |
35 | vdard_bytes_slope | Rate of the number of reading bytes on the vda block device | |
36 | vdawr_reqs_slope | Rate of the number of write requests on the vda block device | |
37 | vdawr_bytes_slope | Rate of the number of write requests on vda the block device | |
38 | vdaerror_slope | Rate of the number of errors in the vda block device | |
39 | hdard_req_slope | Rate of the number of read requests on the hda block device | |
40 | hdard_bytes_slope | Rate of the number of read bytes on the had block device | |
41 | hdawr_reqs_slope | Rate of the number of write requests on the hda block device | |
42 | hdawr_bytes_slope | Rate of the number of write bytes on the hda block device | |
43 | hdaerror_slope | Rate of the number of errors in the hda block device | |
44 | TARGET | Status | Attack/Normal |