Datasets
Standard Dataset
TIPD: Taiwan Indigenous Peoples Open Research Data
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Ji-Ping Lin
- Last updated:
- Sun, 01/23/2022 - 05:05
- DOI:
- 10.21227/jj07-4d71
- Data Format:
- Links:
- License:
 260 Views
260 Views- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
English (for details, see https://osf.io/e4rvz/)
-
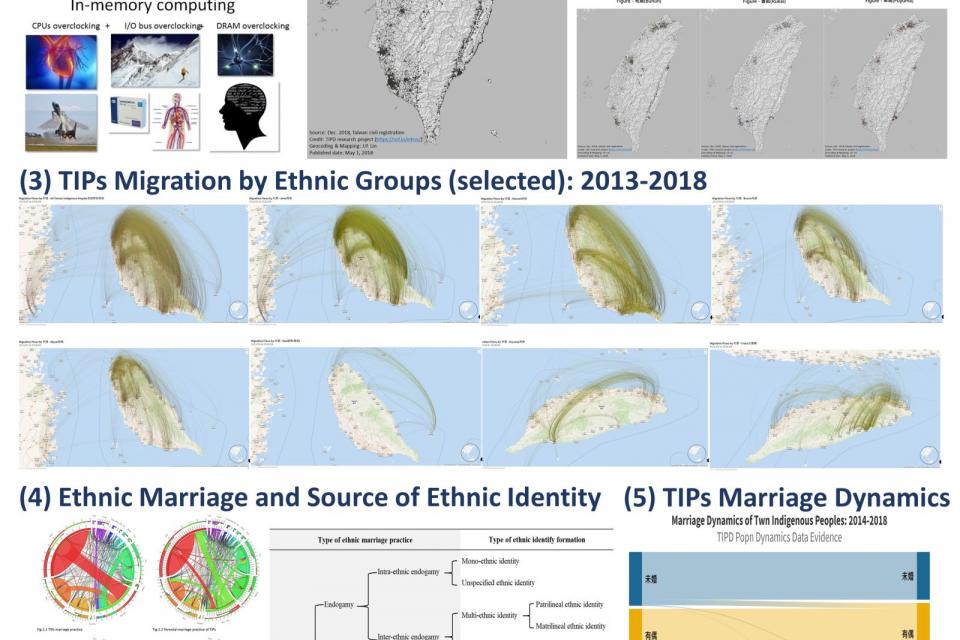
Why the Research and Importance: Taiwan Indigenous Peoples (TIPs) are a branch of Polynesian-Malaysian (or Austronesian) ethnic groups in genetic and linguistic context. Since early 17th Century, TIPs had been playing a crucial role during the Great Marine Times of East Asia trades. There was a rich body of ethnographic, official and academic records on TIPs before 1940. However, the period of 1940-2000 marks as data ”Dark Ages” for TIPs due to 1941-45 Pacific War, 1946-1990 political authoritarian rule in fears of communism and communists infiltration. Persistent lack of TIPs data led TIPs to become isolated, marginalized and thus underdeveloped. Taiwan resumed TIPs population census in 2000 and began recording TIPs individual records in household registration system since 2003. This research program is conducted on the basis of a four-year Joint Research Agreement between Academia Sinica and Council of Indigenous Peoples starting in 2013. One important aim of the research is to construct big anonymous TIPs open research data (or TIPD) based on contemporary census and household registration data sets. TIPD utilizes state-of-the-art data science, record linkage, geocoding, and high-performance in-memory computing technology to construct various dimensions of TIPs demographics & developments. Major outputs of TIPD applications include cross-sectional categorical data, longitudinally constructed population dynamics data, life tables, household statistics, micro genealogy data, intra- & inter-ethnic marriage data, ethnic integration data, ethnic patriarchy and matriarchy identity data, etc. They reflect the progress and efforts of Taiwan academicians struggling to construct various developments of contemporary TIPs. Not only is the research program expected to unveil contemporary TIPs demographics and various developments, but also to help overcome research barriers & unleash social creativity for TIPs studies. They will contribute to shed lights on contemporary population, human dynamics, and developments of TIPs which have been “invisible” to the world for seven decades.
-
Types of TIPD: Major outputs of TIPD which are open to the public amount to 99,184 files in number and around 204 GB in size. TIPD are bilingually documented and its content, context, and volume are growing steadily. TIPD now consist of three categories of open research data: (1) categorical data, (2) household structure and characteristics data, and (3) population dynamics data. Categorical data include four broad dimensions. The first one is contingency tables which are available in PDF, HTML, RTF, XLS formats; the second is multi-dimensional data which are offered in CSV, Excel, dBase, Matlab, Gauss, HTML, JMP, SAS, SPSS, Stata, Access, and R data formats; the third is open data on urban indigenous peoples; the fourth is open data on indigenous traditional tribes/communities. Household structure and characteristics data consist of three broad dimensions of information: (1) household head information, (2) household member composition information, and (3) household geographical information. They are also available in CSV, Excel, dBase, Matlab, Gauss, HTML, JMP, SAS, SPSS, Stata, and R data formats. Population dynamics data consists of three categories: (1) increased population within a given period of time. It can be further dichotomized into two branches of data, population increase due to birth and due to immigration; (2) decreased population within a given period of time. It can also be divided into two branches of data, population decrease due to death and due to emigration; (3) intact population within a given period of time. It can be distinguished into two categories of population: those who make internal migration and those remaining staying-put. For intact population who make internal migration, internal migration processes such as in-, out-, net, gross migrations are analyzable. Every types of population dynamics data are available in CSV, Excel, dBase, Matlab, Gauss, HTML, JMP, SAS, SPSS, Stata, Access, and R data formats. The potential applications for research on TIPs based on TIPD include studies on birth, death, migration, residential mobility, life table, marriage, ageing, education, medical care, labor, family, community, etc. TIPD could be used as background data for survey study, including population analysis, sampling design and sampling planning. TIPD also offers additional open data for specific research purpose, including (1) indigenous tribal data in traditional territories, (2) indigenous communities in urbanized areas, and (3) aggregated population centers at various geographic units.
-
Potential contributions: TIPD reflects the progress and efforts of Taiwan academicians struggling to construct various developments of contemporary TIPs population. The potential applications for research on TIPs based on TIPD include studies on birth process, death process, migration process, residential mobility, life tables, marriage, ageing, education, medical care, labor, family, community, etc. TIPD could be used as background data for survey study, including population analysis, sampling design and sampling planning. Not only does TIPD help unveil contemporary TIPs demographics and various developments, but it also helps overcome research barriers and unleashes creativity for TIPs studies. It will help shed light on contemporary population, human dynamics, and developments of TIPs which have been “invisible” to the world for seven decades. TIPD potential contributions are threefold. First, theoretically based on data science, not only does TIPD overcome legal and ethical issues, but it also democratizes the use of detailed information hidden in modern micro data sets. Thus it is expected to promote research and unleash creativity in the context of TIPs studies and to enhance the visibility of TIPs. Second, TIPD empirically demonstrates that the value-added data enrichment and open data sharing could be accomplished by using less expensive digital infrastructure and open data repository. Third, in addition to general-purpose research, TIPD enables us to conduct very specific researches, such as population dynamics, family life course, life table, ethnic relationship, etc. In short, the potential contributions of TIPD are as follows. First, a contribution of moving from “closed” to “open” in the sense that the research on TIPD helps shed light on contemporary Taiwan Indigenous Peoples and human dynamics which have been “invisible” to the world for seven decades. Second, a contribution of moving from “the elite” to “the ordinary” in the sense that the constructed open data sets reduce tech barriers for researchers interested in indigenous population studies. Third, a contribution of moving from “local” to “global” in the sense that the English version of TIPD is open to the international academic community to promote further value-added data enrichment through international collaboration. Fourth, a contribution of enabling TIPs research from “macro and static” to “micro and dynamic” data by providing, e.g., micro social network data, genealogy, and population dynamics open data
繁體中文 (細節請參考 https://osf.io/e4rvz/)
- 研究緣起及重要性:台灣原住民族屬南島民族,不僅社會及文化多元,族群及語言多樣,自大航海時代以降,亦在東亞經貿扮演要角,歷史文獻眾多。近代以科學及系統化方式記錄台灣原住民族基礎資料始自日治時期,包括人口普查、户籍登錄及調查,但至太平洋戰爭爆發而終止。1940年代初始至公元2000年,係台灣原住民族基礎資料付諸厥如之「黑暗時代」。主要原因包括日治後期太平洋戰爭、戰後治權移轉及治理混亂、國共內戰保安思維延續及擴大至原鄉、和強調單元文化主義。戰後原住民族基礎資料之缺乏,導致原住民族學術研究及各類政策規劃和設計無所依據,難以科學方法進行系統化研究;該情況亦導致原住民族陷入更加孤立與隔絕,使原住民族各類發展難以和現代化過程銜接。基礎資料長期之缺漏,原住民族終將變成過去歷史記憶,並失去現代性及未來發展性。解嚴後及1990年代,眾多先進努力下,公元2000年户口及住宅普查恢復蒐集原住民族基本資料,是為近代原住民族基礎資料之重大里程碑。爾後原住民身分法公布,戶政系統開始加註原住民族戶籍登錄資料,歷經十多年之精進,公元2010年後原住民族公務登記資料之內容和品質已日趨完備。台灣原住民族是台灣過去發展長期被忽略及忽視的主角,今日之記錄必成明日之史料,未來之發展無法脫離過去之軌跡。本研究計畫目的之一是以原住民族現代公務登記資料為基礎,以保障隱私、合乎法律規定、及倫理規範為前提,定期保存原住民族現代公務登錄資料,並運用現代科技及先進計算技術,以科學方法系統化及自動化方式,進行基礎資料加值和基礎統計量運算。研究亦以開放之精神,成果將公開供國內外產官學專家参考及運用,期許有助彌補過去原住民族基礎資料缺失之憾,對目前及未來原住民族基礎資料保存和運用,及促進多元文化發展和各族群相互理解,略盡棉薄之力。
-
資料種類及內容:TIPD目前計99,184個共約204GB開放學術研究資料,以中文及英文描述,研究資料內容、種類、及規模將持續增加之中。目前主要開放研究資料類型包括:(1)類別資料(或稱離散資料),(2)家戶結構資料,(3)人口動態資料等三大類型。類別資料再分成兩大類:(a)列聯表(或所謂交叉表),含PDF、HTML、RTF、XLS四個基本格式;(b)多維表,含CSV、Excel、dBase、Matlab、Gauss、HTML、JMP、SAS、SPSS、Stata、Access、R等格式;(3) 都市原住民開放資料;(4) 傳統部落/社區開放資料。家戶結構資料包括三個基本面向:(1)戶長基本資訊、(2)家戶成員組成資訊、(3)家戶環境變數資訊,亦以CSV、Excel、dBase、Matlab、Gauss、HTML、JMP、SAS、SPSS、Stata、Access、R等格式呈現;人口動態資料分成三大類:(1)兩時點間”增加人口”,可區隔”出生”及”跨國移入”因素、(2)兩時點間”減少人口”,亦可區隔”死亡”及”跨國移出”因素、(3)兩時點間”持續存活人口”,可區隔”沒做內部遷徒(stay-put)”及”有做內部遷徒”因素,內部遷徙亦可分析”移入”及”移出”等要素,人口動態資料亦以多維表資料呈現,含CSV、Excel、dBase、Matlab、Gauss、HTML、JMP、SAS、SPSS、Stata、Access、R等格式。TIPD開放研究資料庫可當質性或量化研究之專業或背景資料,主要潛在應用領域包括出生、死亡、人口遷徙、家戶流動、生命表、婚配、老化、教育、醫療、照護、勞動、家庭、社區,亦可做為母體分析、抽樣設計及抽樣規劃等參考依據。TIPD亦提供特定用途的開放研究資料,包括(1) 都市原住民開放研究資料、(2) 傳統部落及社區基礎資料、(3)各類人口重心資訊(包括區域、縣市、鄉鎮市區、村里、都會區、部落)。
-
潛在貢獻:如下(1).幫助學術研究及民間部門克服資料取得之障礙及促進研究效率,並間接促進當代原住民研究:當代原住民研究最大障礙之一是缺乏大規模及系統性之基礎資料,本資料庫預期能幫助學術及研究部門克服基礎研究資料取得之障礙,大幅減少學術及行政部門間資料索取及處理之行政成本,由於開放資料庫亦包含各類資料格式,可供學術研究者直接進行資料分析,故預期可促進學術研究效率及產出,促進現代原住民學術研究,例如自104年11月全面開放本資料庫供各界下載使用後,許多以前難以進行之基礎研究目前得以進行,由長期角度來看,本資料庫幫助學術及研究部門克服基礎研究資料取得之障礙後,預期能有助未來累積大量的研究成果,並回饋原住民政策規劃及設計。(2).大幅減少未來提供及管理基礎資料之行政成本,及促進政策設計及規劃效率:本資料庫之建構學理基礎係奠基於資料科學,以自動化方式系統性產生合乎法律及倫理規範之開放資料庫。該開放資料庫可做為中央及地方各級政府政策規劃及決策之背景資料,能有效大幅減少各部門間資料索取公文往返行政成本、並直接運用在輔助政策規劃及決策,故預期能大幅減少行政成本及促進政策設計及規劃效率。(3).已完成特定議題之專業資料庫,使得特定專業議題之研究及政策規劃設計可以進行,包括人口變遷、家庭、都市原住民、出生、死亡、遷徙、婚配、生命表、教育、社區、族群關係等專業特定議題。
Both files use tree structure to exhibit TIPD repository structure and files under a give directory in TIPD repository.
Documentation
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| 4.56 MB | |
| 428.03 KB |