Datasets
Standard Dataset
Syphilis and Tourism and Geographic Location Dataset - SyphTGL
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Joberto S Martins
- Last updated:
- Sat, 12/07/2024 - 11:29
- DOI:
- 10.21227/0y08-y911
- Data Format:
- Links:
- License:
 204 Views
204 Views- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
Tourism is increasing worldwide and has many benefits for countries and cities, such as creating jobs, increasing company revenue, and improving government tax collection. As such, tourism is an unstoppable trend followed by countries and municipalities that try to stimulate this activity. However, unexpected impacts of this, in principle, wealthy activity must be observed.
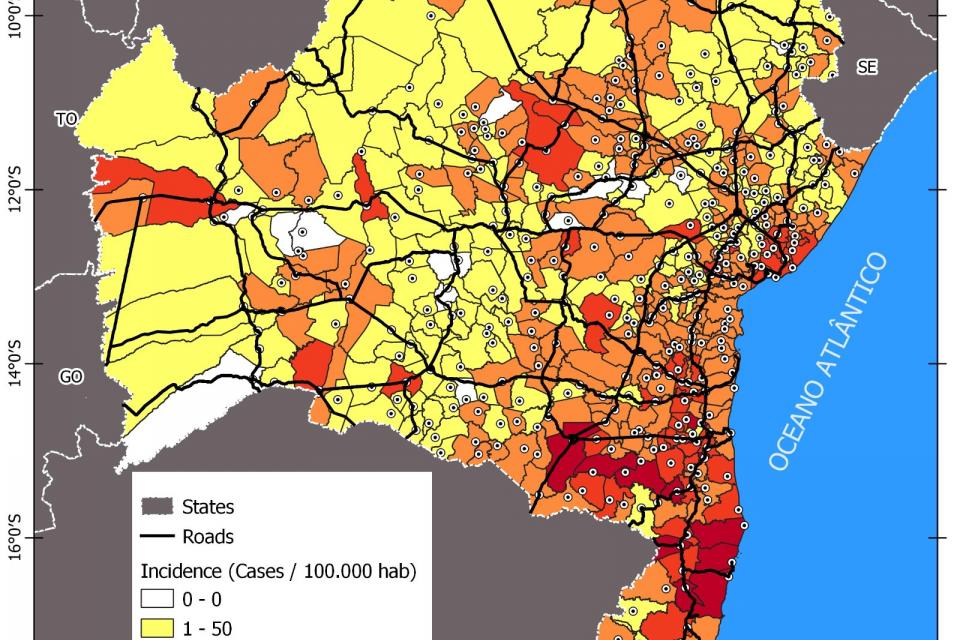
This is the dataset for the paper "Evidence Analysis of Tourism and Geographic Location Correlation with Syphilis Incidence in Bahia State—Brazil." It contains a valuable set of data and information concerning the incidence of syphilis in Bahia state, Brazil, for 10 years, suitable for machine learning algorithm analysis. A KMeans clustering analysis database is included in the dataset.
SYPHILIS DATASET
This syphilis incidence dataset is used in the paper "Evidence Analysis of Tourism and Geographic Location Correlation with Syphilis Incidence in Bahia State - Brazil".
The syphilis dataset is composed of a set of datasets as follows:
• SyphTGL1: Syphilis Incidence
• SyphTGL2: Syphilis Incidence Normalized
• SyphTGL3: Syphilis Incidence Clustering
The SyphTGL1 dataset is the basic dataset containing data concerning governmental syphilis notification (incidence) in Bahia state, Brazil, by municipality from 2019 to 2020. It was provided by the Ministério da Saúde/SVS - Sistema de Informação de Agravos de Notificação - Sinan Net and is publicly available at https://portalsinan.saude.gov.br/. Syphilis incidence analysis is performed in the context of the Smart and Sustainable City initiative (Martins, 2018, Farid et al., 2021a, Farid et al., 2021b).
The SyphTGL2 dataset is the normalized dataset resulting from SyphTGL1 processing to allow the KMeans clustering. For the clustering process, the following processing and additional information are considered:
• A municipality tourism categorization; and
• The normalization of the syphilis incidence and binary encoding of variables, such as tourism category.
2
The municipality tourism categorization is defined by the Ministry of Tourism of Brazil (MinistérioDoTurismo, 2024) and has the following categories:
• Municipality type "A": Municipalities with complete tourist infrastructure, a wide variety of attractions, high tourist flow, and efficient management. It corresponds to a highly touristic municipality;
• Municipality type "B": Municipalities with good infrastructure, diversified tourist attractions, moderate tourist flow, and developing management;
• Municipality type "C": Municipalities with basic infrastructure and tourist attractions are present but have potential for development, and the tourist flow is still growing;
• Municipality type "D": Municipalities with limited infrastructure, incipient tourist attractions, and low tourist flow;
• Municipality type "E": Municipalities with less tourist potential, generally with few attractions and precarious infrastructure; and
• Municipality type "F" - a municipality with no tourist flow or capabilities.
The SypyTGL3 dataset contains basic information concerning the municipalities and the KMeans clustering execution run executed for the SyphTGL2 dataset.
REFERENCES
Farid, A. M., Alshareef, M., Badhesha, P. S., Boccaletti, C., Cacho, N. A. A., Carlier, C.-I., Corriveau, A., Khayal, I., Liner, B., Martins, J. S. B., Rahimi, F., Rossett, R., Schoonenberg, W. C. H., Stillwell, A., & Wang, Y. (2021a). Smart City Drivers and Challenges in Urban-Mobility, Health-Care, and Interdependent Infrastructure Systems. IEEE Potentials, 40(1), 11–16.
Farid, A. M., Alshareef, M., Badhesha, P. S., Boccaletti, C., Cacho, N. A. A., Carlier, C.-I., Corriveau, A., Khayal, I., Liner, B., Martins, J. S. B., Rahimi, F., Rossett, R., Schoonenberg, W. C. H., Stillwell, A., & Wang, Y. (2021b). Smart City Drivers and Challenges in Urban-Mobility, Health-Care, and Interdependent Infrastructure Systems. IEEE Potentials, 40(1), 11–16.
Martins, J. S. B. (2018). Towards Smart City Innovation Under the Perspective of Software-Defined Networking, Artificial Intelligence and Big Data. Revista de Tecnologia da Informação e Comunicação, 8(2), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1467771
MinistérioDoTurismo. (2024). Portal de Dados Abertos. Retrieved November 9, 2024, from https://dados.gov.br/dados/conjuntos-dados/categorizacao
Dataset Files
- SyphTGL1: Syphilis Incidence SyphTGL1 - Syphilis Incidence.csv (9.48 kB)
- SyphTGL2: Syphilis Incidence Normalized SyphTGL2 - Syphilis Incidence Normalized.xlsx (34.46 kB)
- SyphTGL3: Syphilis Incidence Clustering SyphTGL3 - Syphilis Incidence Clustering.xlsx (42.63 kB)
Documentation
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| 55.53 KB |