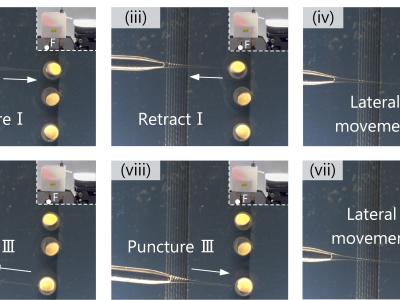
An untethered ultrasonic robot (U2sonobot) operating in resonant vibration is developed by integrating dual transducers, an onboard circuit, and a battery. Here, the longitudinal and bending vibrations lead to the out-of-phase swing motion and the alternating acceleration, respectively; these imitate the rotatory galloping gait in terms of the driving feet’s movement pattern and the operating sequence. First, the transducers were designed to gather the resonant frequencies of two vibrations and produce the same node for steadily supporting the other components.
- Categories: